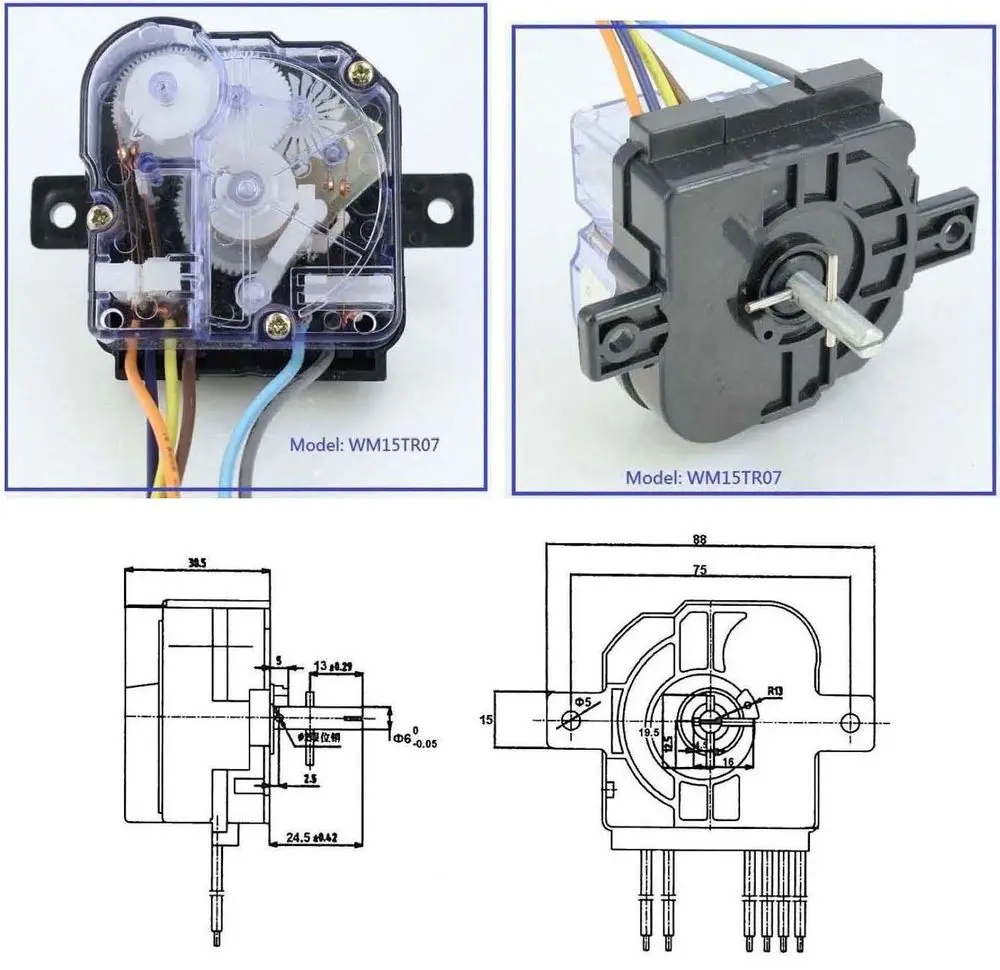
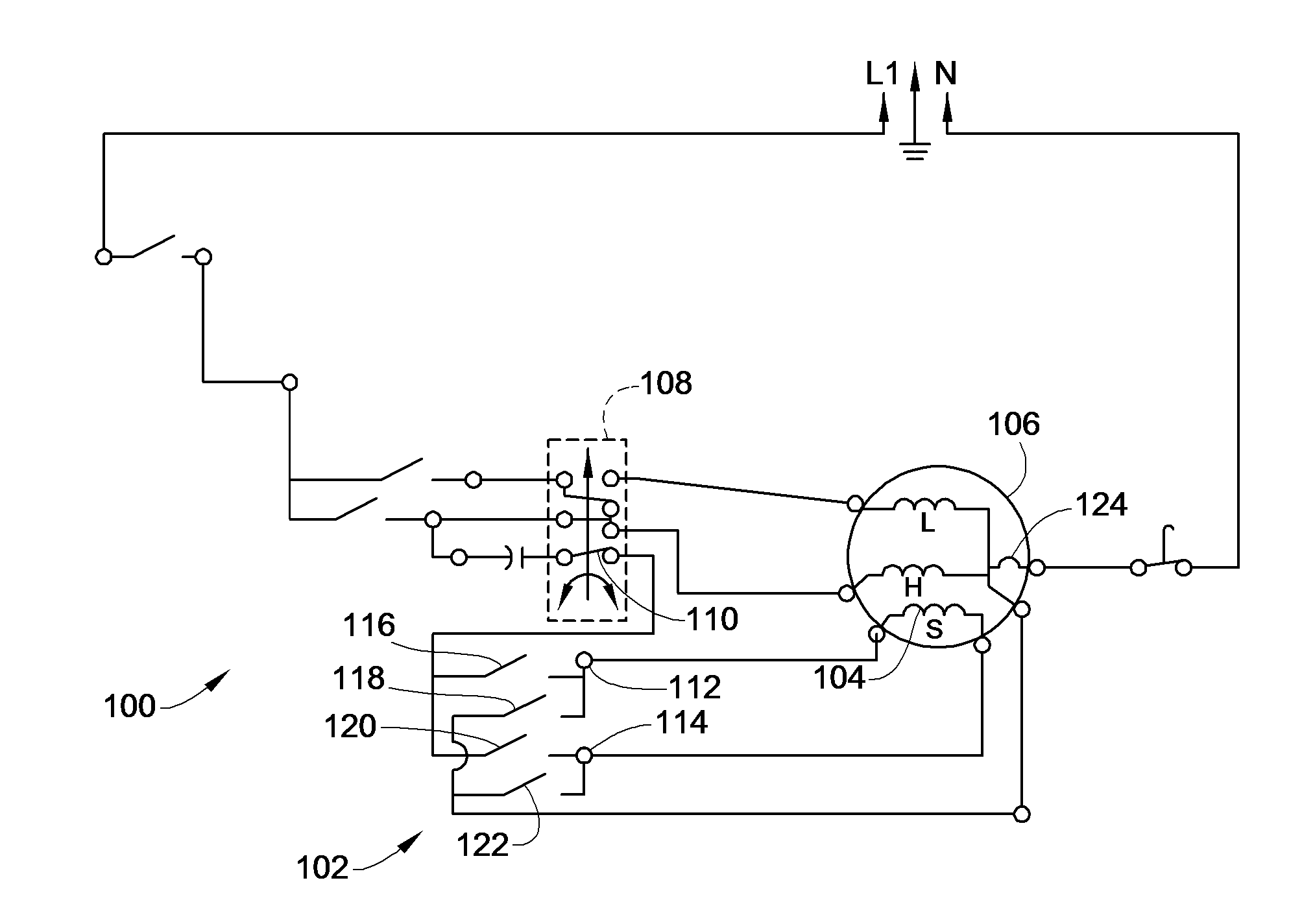
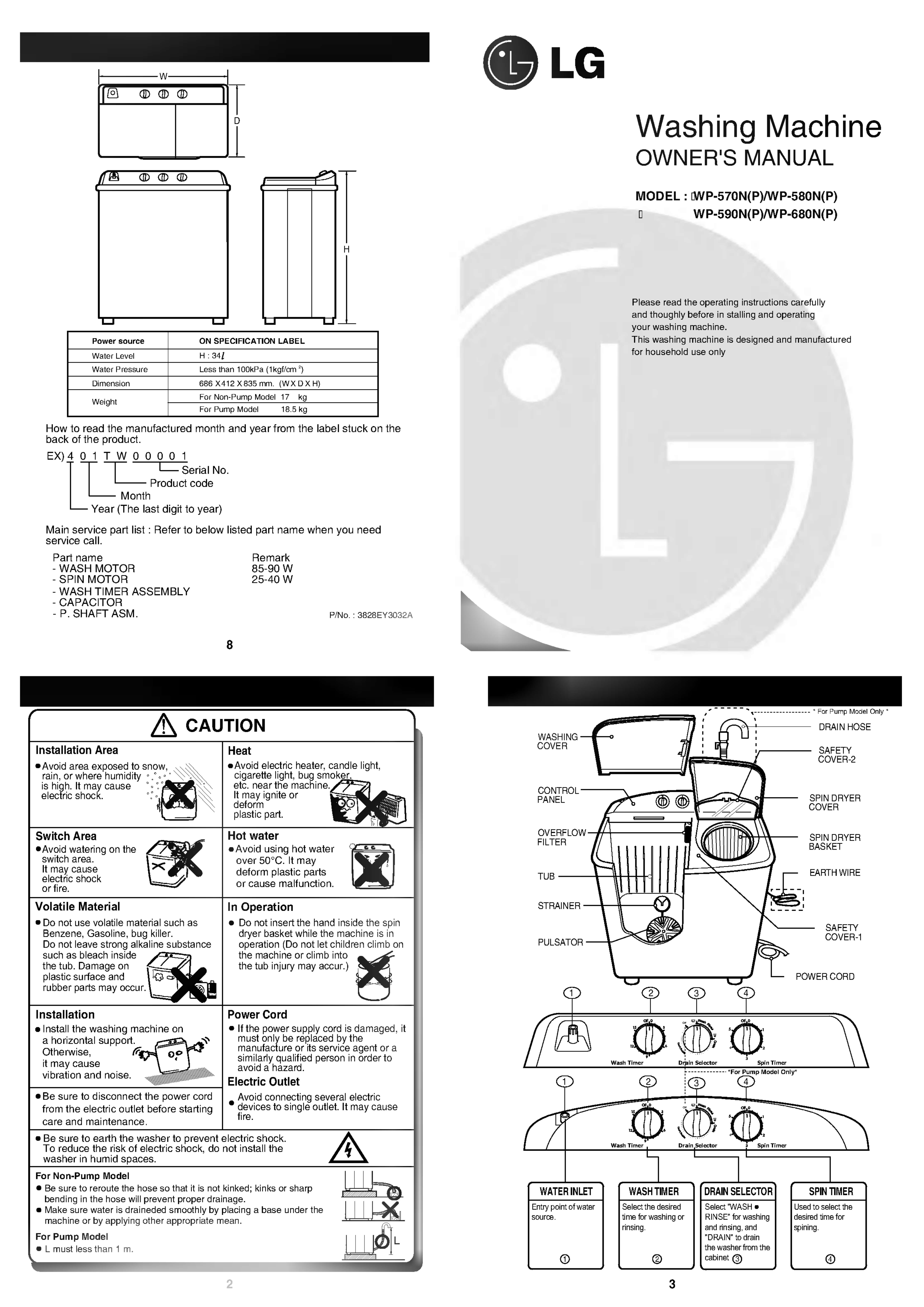
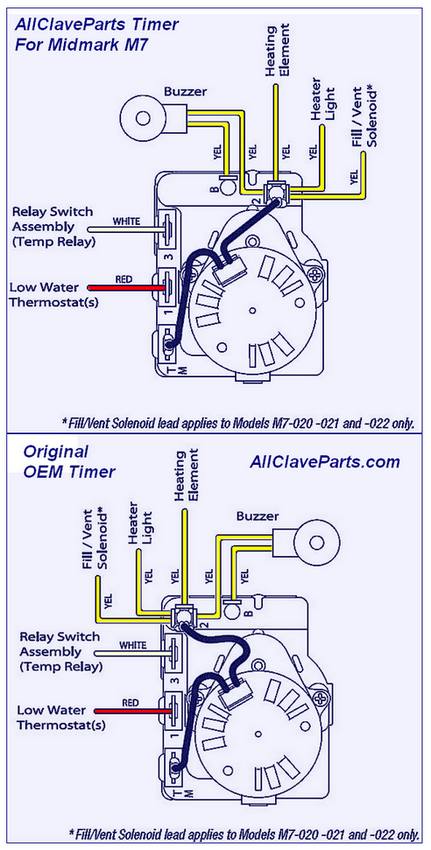
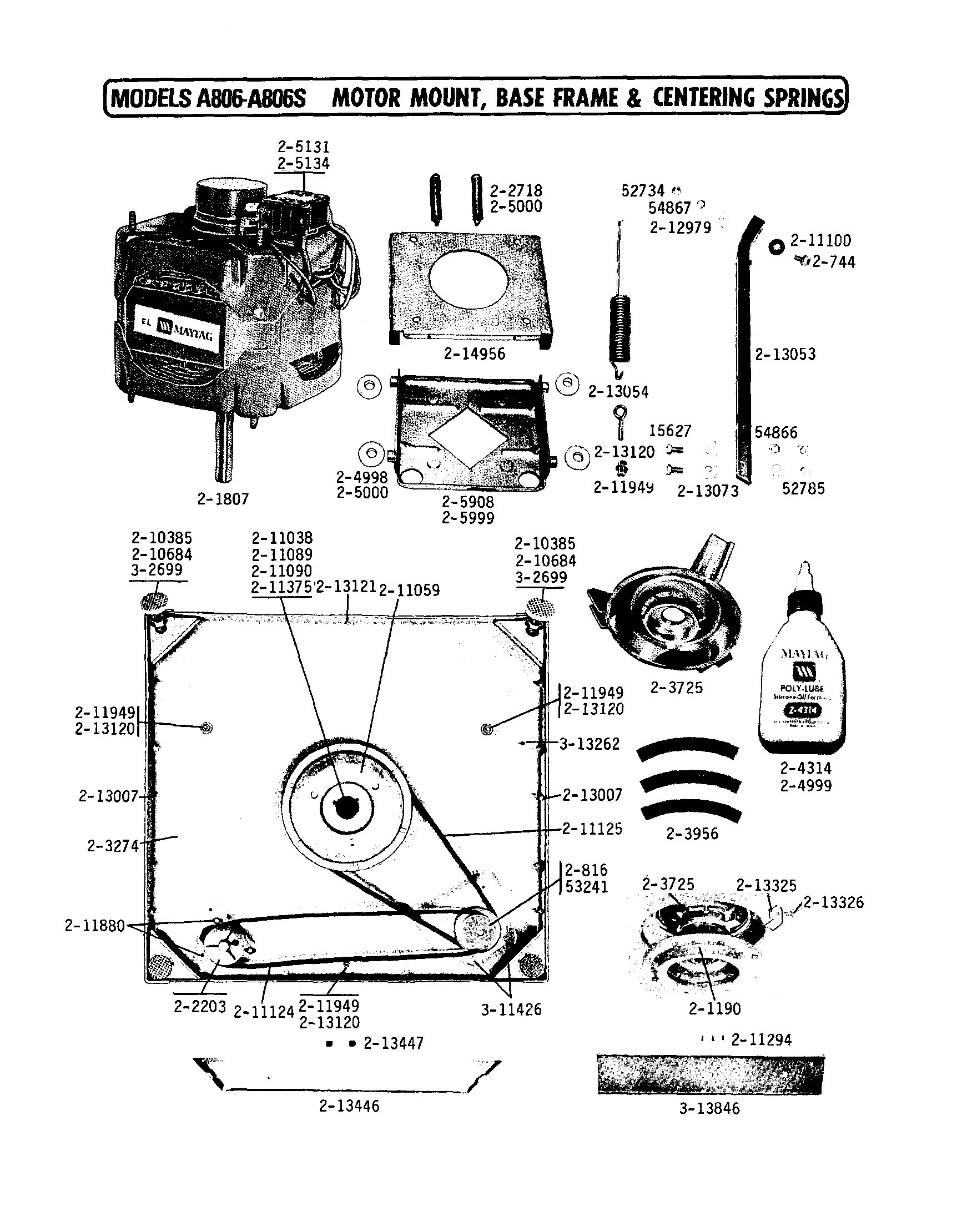
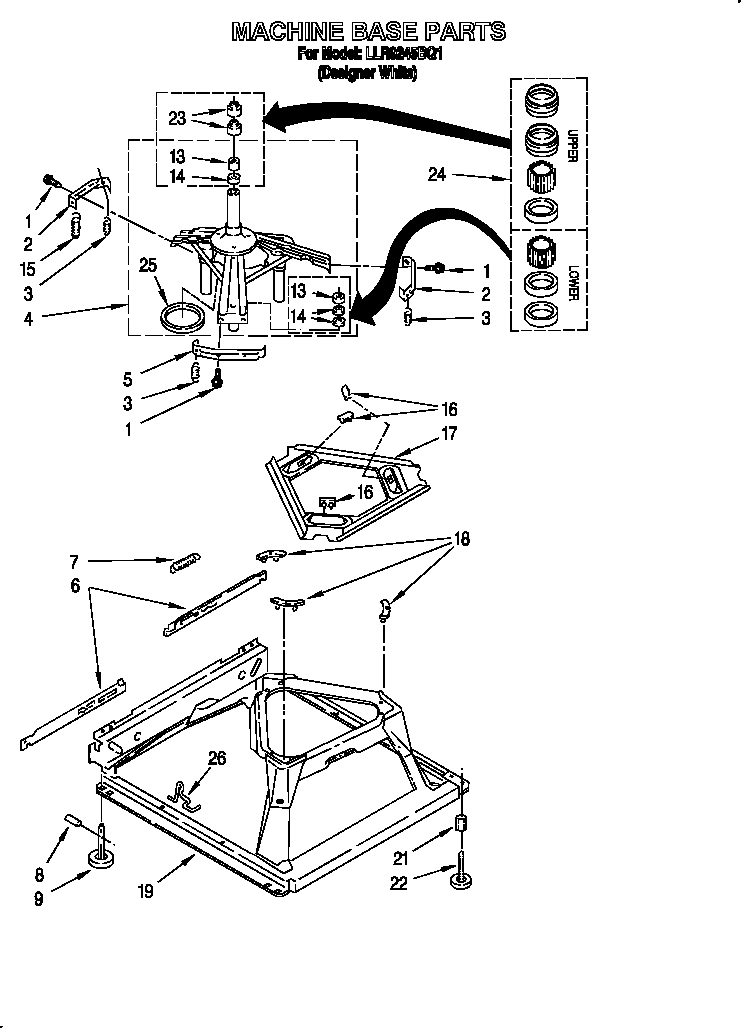
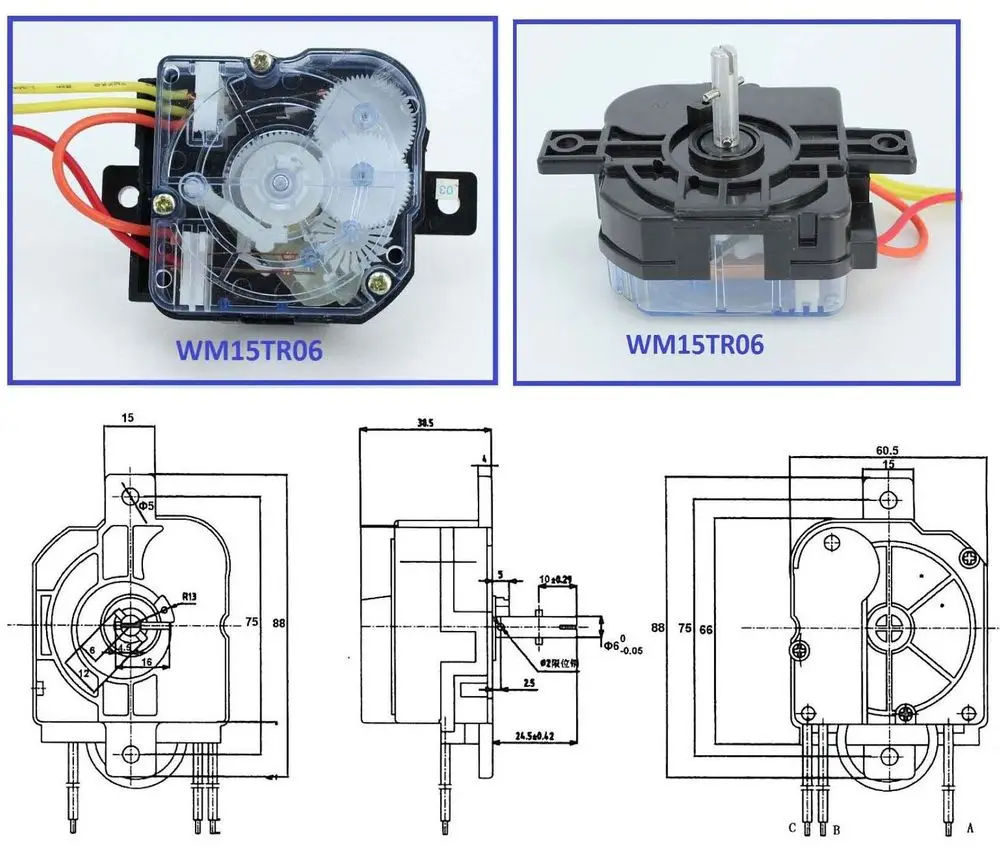
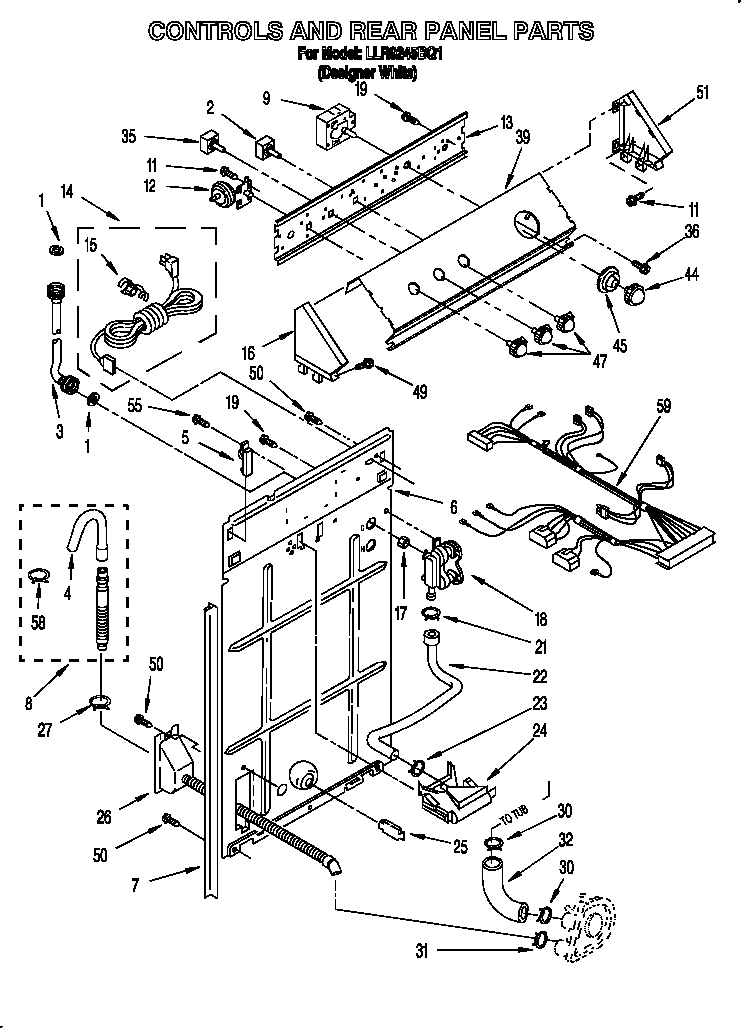
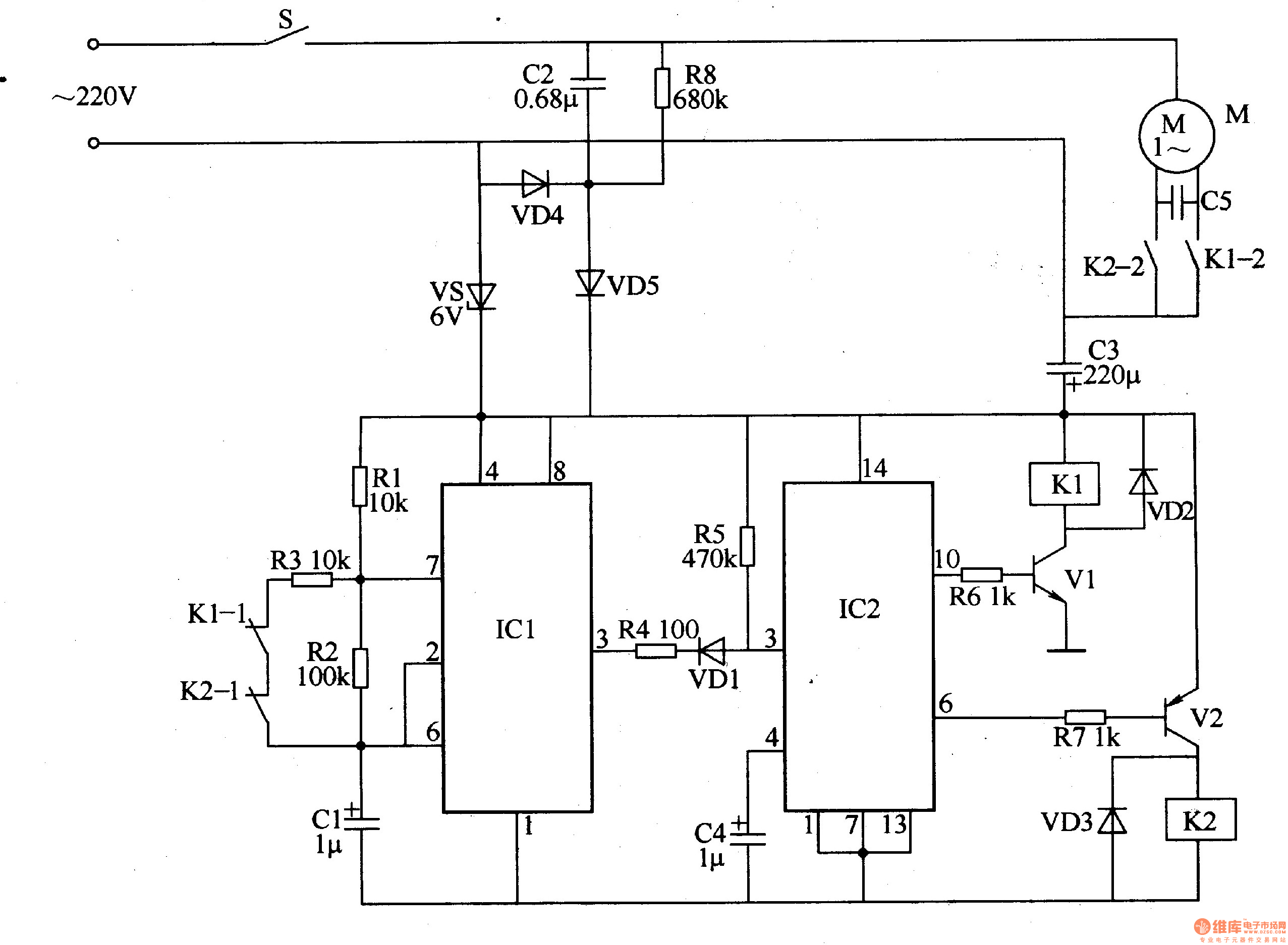
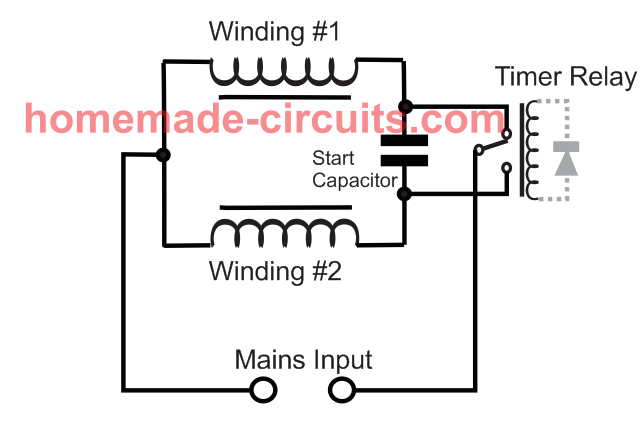
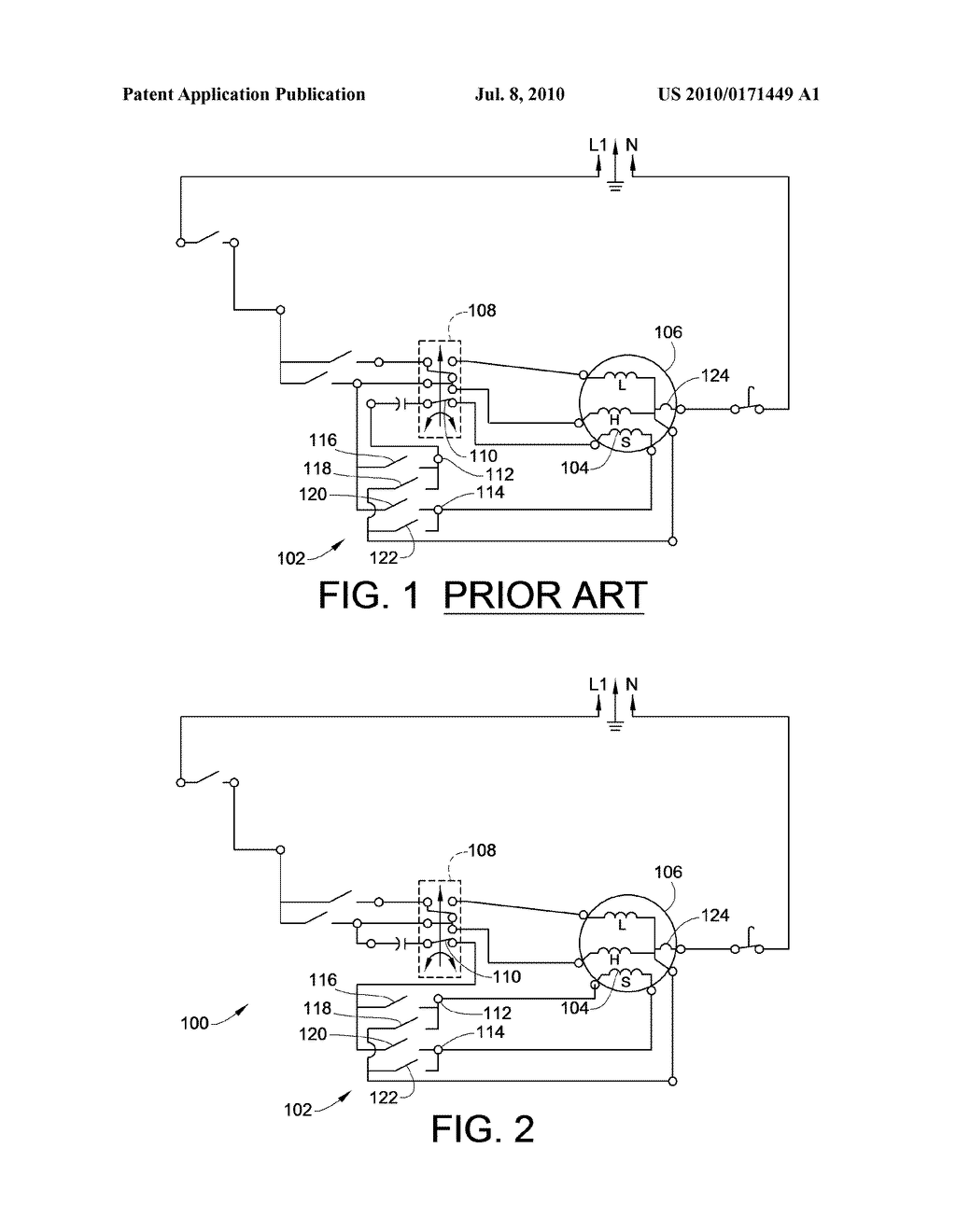
Circuit blueprints are the visual code of electricity. They convert complex electrical systems into structured symbols that allow engineers and enthusiasts to understand how a circuit functions. Yet for many beginners, these diagrams can appear confusinga maze of lines, arrows, and abbreviations. The purpose of Washing Machine Timer Wiring Diagram is to transform that confusion into comprehension by teaching you how to read, interpret, and apply wiring diagrams effectively, anywhere in Wiring Diagram or beyond (http://mydiagram.online, 2026, https://http://mydiagram.online/washing-machine-timer-wiring-diagram/MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE).
At its core, a wiring diagram represents the interaction between components in a circuit. Every line, symbol, and label carries meaning. A line indicates a conductor carrying current; a dot marks a junction; arrows show the direction of flow; and symbols represent devices such as switches, relays, sensors, or motors. Learning to decode these symbols is the first step toward understanding the underlying logic of any electrical system.
Before diving into the details, its important to grasp the concept of **circuit flow**. Electricity always travels in a closed loopfrom the power source through the load and back to ground. A typical schematic displays this flow from top to bottom or left to right, showing how power moves through fuses, switches, and connectors before reaching the final component. Tracing this flow visually helps identify where power begins, where its controlled, and where it returns.
A well-structured wiring diagram is like a roadmap. Each path leads to a specific destinationperhaps a light bulb, motor, or control module. To follow the map, start at the power source and trace through each device until you reach ground. Along the way, note any branching connections, as they indicate circuits that share the same power supply or control signal. By mentally following the path of current, youll gain insight into how the system operates and where issues may occur.
**Symbols** are the vocabulary of this electrical language. A resistor, for instance, is drawn as a zigzag line, while a diode appears as a triangle pointing to a bar. Capacitors, transistors, and integrated circuits all have unique shapes. In automotive and industrial schematics, standardized symbols are governed by international organizations such as **IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission)** and **ANSI (American National Standards Institute)**. Once you learn these conventions, you can read almost any schematic regardless of manufacturer or regionincluding those used in Wiring Diagram.
Color codes and wire labels add another layer of meaning. Each wire may carry a marking like BLK/YEL (black with a yellow stripe) or GRN/WHT (green with white). These markings indicate wire purpose, polarity, or connection point. Some systems use numerical codes to match connectors and harnesses. Understanding this labeling system allows you to correlate whats on paper with the real wiring inside a machine or vehicleturning documentation into a living guide.
Another key concept is recognizing **reference designations**. Every component is labeled with an identifierR1 for resistor, K3 for relay, S2 for switch. These match the parts list in the manual, making it easier to locate specific items during assembly or repair. A technician who can quickly cross-reference these details saves significant time in maintenance and diagnostics.
Interpreting **signal flow** is another major step. In modern systems, not all circuits carry raw voltage; many transmit **digital signals** or **data communication** between modules. For example, a sensor might send a variable voltage signal to an ECU, which then outputs a pulse-width-modulated (PWM) signal to an actuator. Schematics often show waveform symbols or directional arrows to indicate these signals. Recognizing them helps you separate power circuits from logic circuitsan essential distinction when troubleshooting in Washing Machine Timer Wiring Diagram.
Practical reading also involves understanding **connectors and pinouts**. Each connector in a schematic corresponds to a physical plug or socket. Pin numbers indicate wire positions inside the connector housing. During repair, technicians use this data to back-probe or check continuity with a multimeter. Misreading a pin number can cause major confusion, so always double-check orientation and labeling before assuming a fault.
In large schematics, different pages represent sections of the same system. Cross-references such as See Sheet 3, Connector C-21 link those pages. Follow them carefully to trace the full circuit path. Many professionals use digital markup tools or colored highlights to mark whats been checkedan efficient habit for those who handle complex multi-page documents.
Finally, true mastery comes from combining **theory and practice**. Its one thing to recognize symbols on paper; its another to understand what actually happens in the circuit. Reading the schematic should allow you to predict voltage at any test point, locate potential faults, and confirm signal flow with real measurements. Every successful diagnosis begins with correct interpretation.
By consistently comparing wiring diagrams with real circuits, youll develop what professionals call **electrical vision**the ability to see how electrons move invisibly through switches, modules, and wires. Over time, a schematic becomes more than just a pictureit becomes a living map of logic, power, and communication that guides every repair, design, and innovation. Once you reach that level of understanding, you wont just read wiring diagrams; youll *think* in themspeaking the universal language of electricity, refined through the Washing Machine Timer Wiring Diagram project in 2026 under http://mydiagram.online.