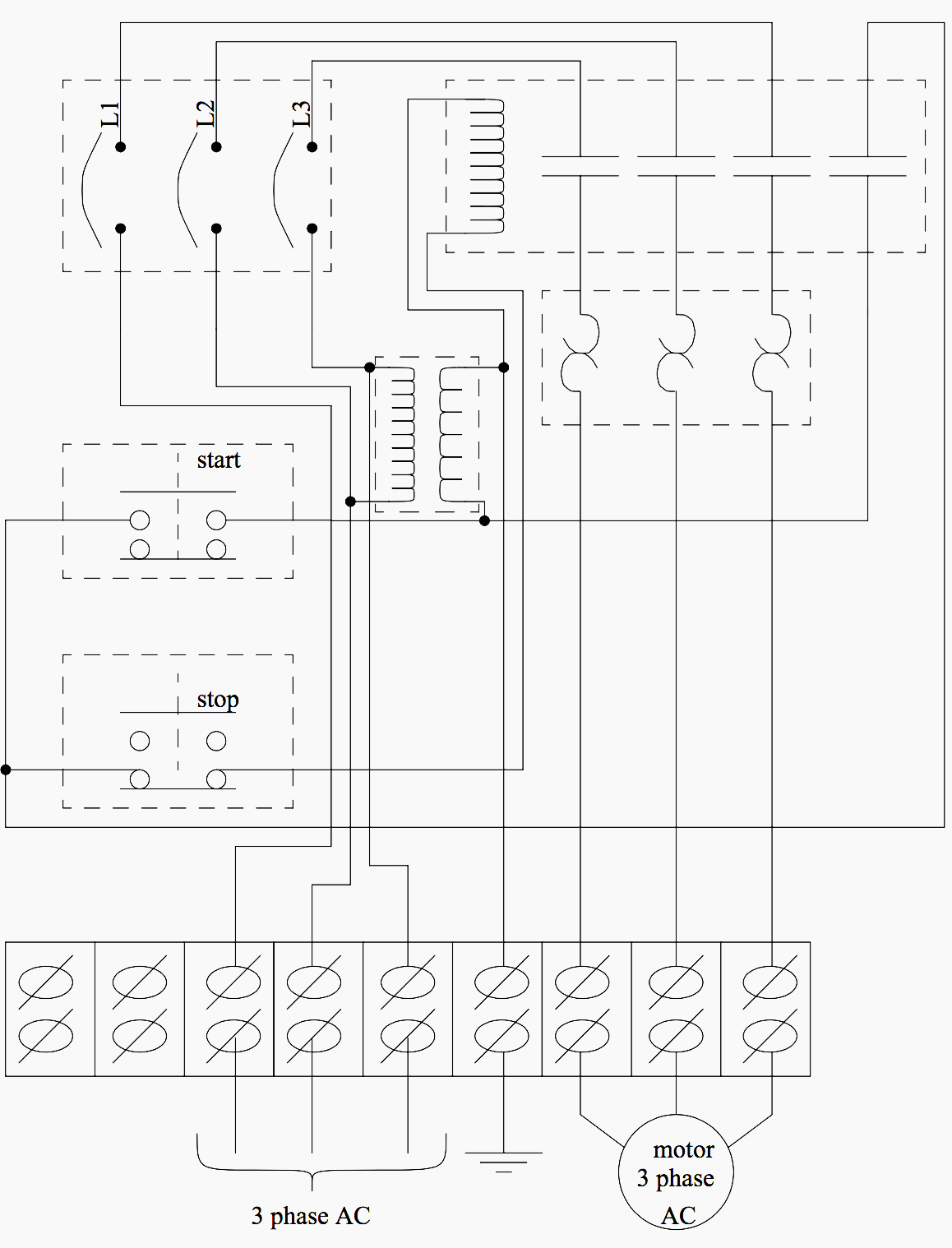
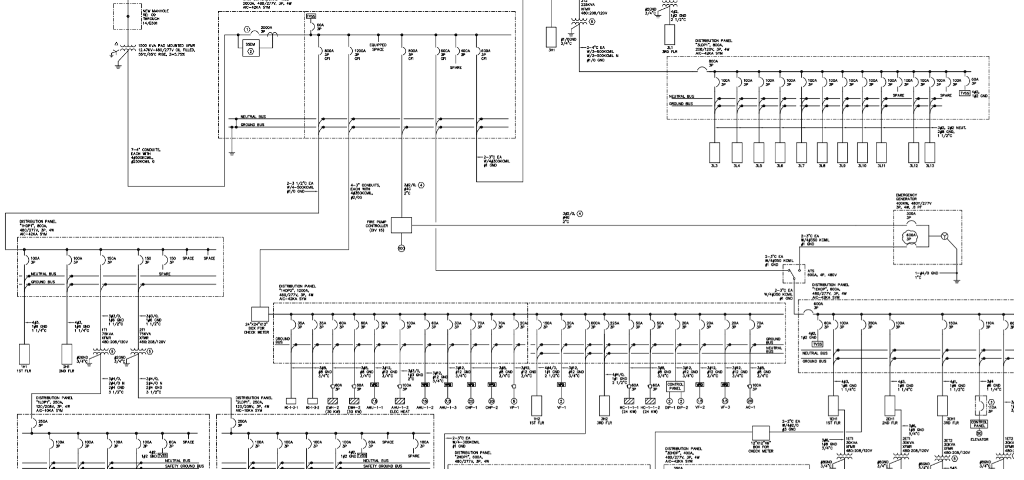
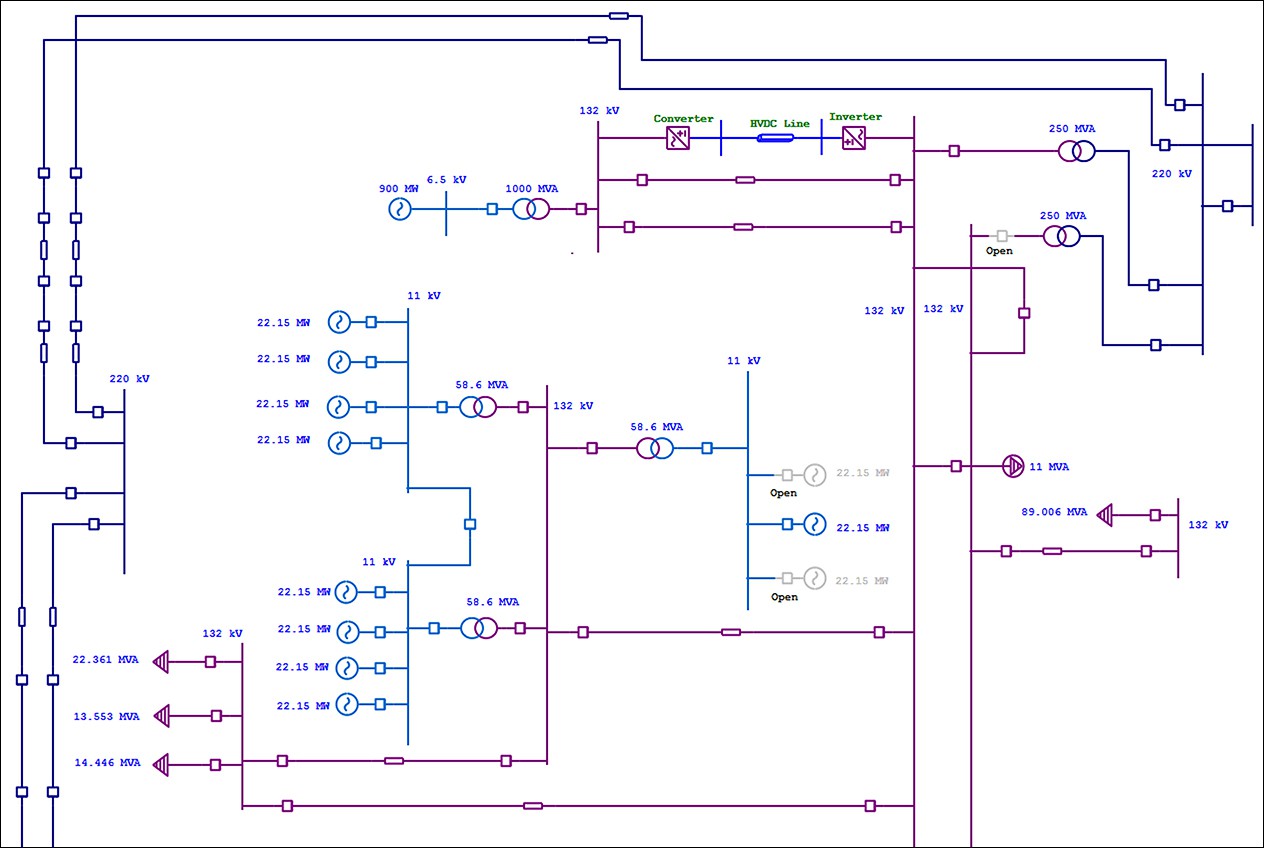
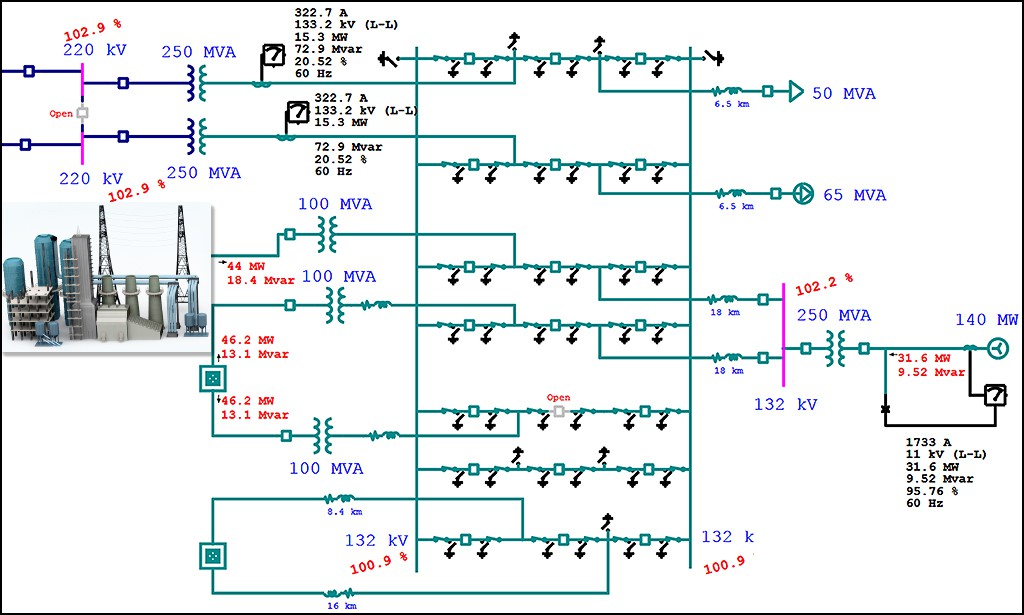
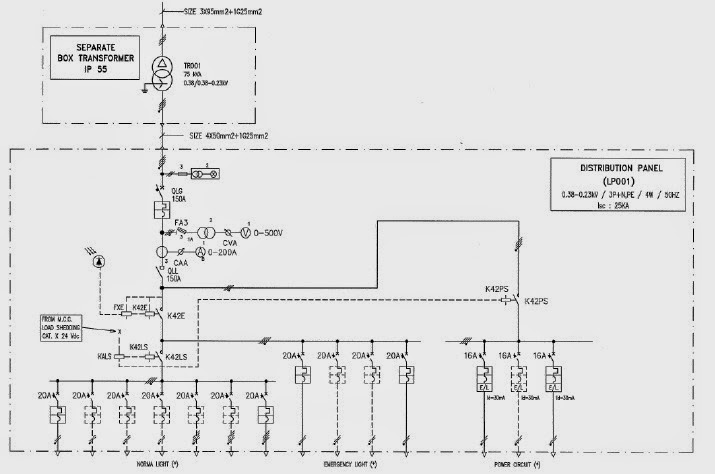
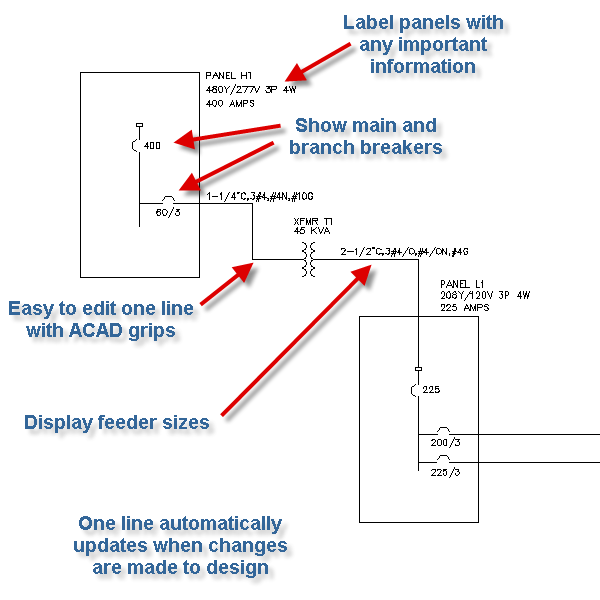
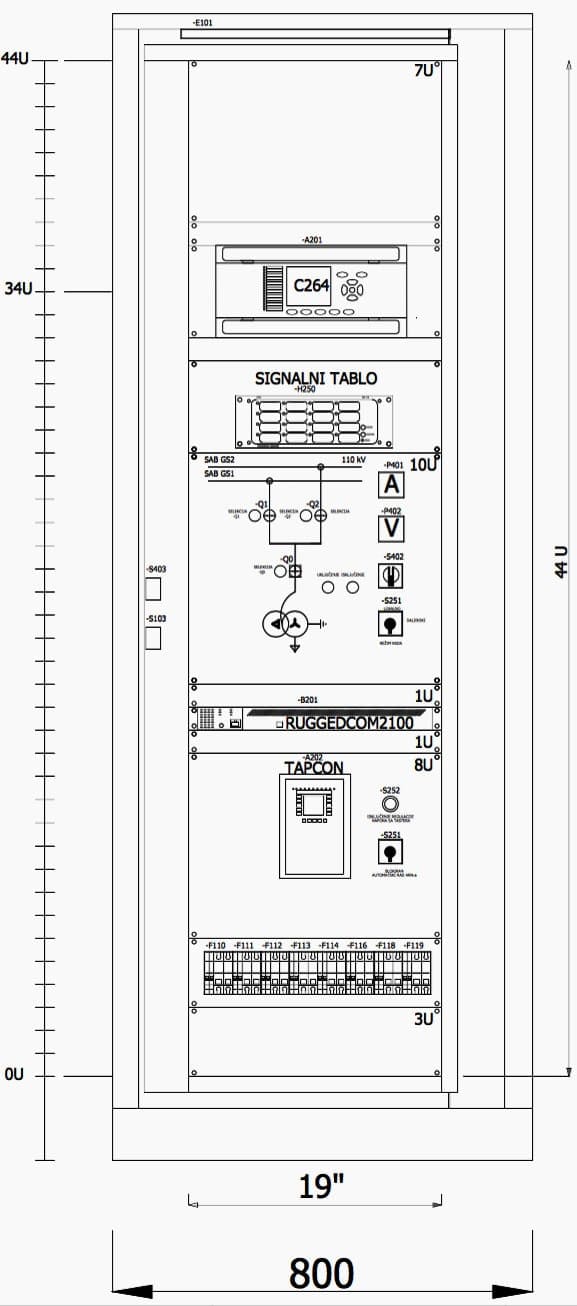
As technology advances in electrical and control systems, traditional individual signal cabling can no longer handle the rising volume of signals efficiently. Modern wiring networks therefore rely on communication protocolsdefined sets of rules that determine how devices exchange information. These methods have transformed wiring from simple power and signal links into smart, digital communication infrastructures capable of synchronization, feedback, and control.
At its essence, a communication protocol defines how data is formatted, transmitted, and interpreted. Rather than each sensor and actuator needing its own cable, multiple devices can share a single bus or network line. This drastically reduces wiring complexity while improving system efficiency and flexibility. The protocol ensures that, even though devices share the same conductors, their messages remain distinct and error-free.
One of the most widespread examples is the Boschs CAN system. Originally developed by Bosch in the 1980s, CAN allows microcontrollers and sensors to communicate without a central host. It uses a priority-driven structure where all nodes can transmit and listen simultaneously. Data priority is managed by identifier ranking, ensuring that high-priority datasuch as real-time control parametersalways takes precedence. Its durability and reliability make it ideal for high-interference installations.
Low-cost Local Interconnect Network serves as a simplified companion to CAN. While CAN handles high-speed, mission-critical data, LIN connects less demanding components such as lighting controls and simple actuators. Operating under a master-slave scheme, one central node manages the communication timing of all others. LINs simplicity and low cost make it an ideal choice for secondary subsystems that complement high-speed CAN networks.
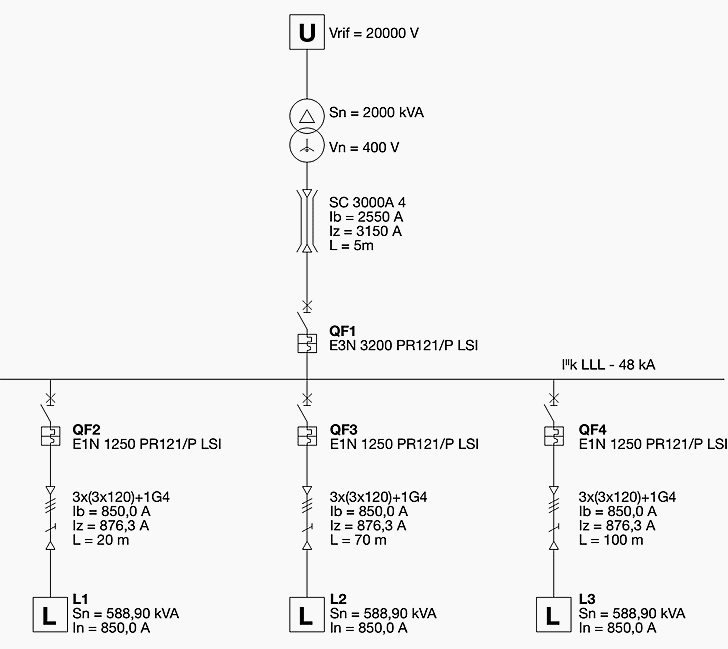
In industrial automation, Modbus and Profibus dominate. Modbusamong the oldest communication systemsis valued for its openness and simplicity. It transmits data via serial lines like RS-485 and remains popular because of its wide support across PLCs, sensors, and HMIs. Process Field Bus, meanwhile, was designed for higher performance and synchronization. It employs deterministic communication to coordinate hundreds of devices on a single network, offering both factory automation and process control.
As Ethernet became more accessible, industries migrated toward real-time Ethernet-based systems such as PROFINET, EtherCAT, and EtherNet/IP. These technologies combine speed and flexibility with deterministic timing needed for real-time control. For example, EtherCAT processes data **on the fly** as it passes through each node, reducing latency and achieving sub-millisecond precision. Such efficiency makes it ideal for robotics, CNC machines, and automation lines.
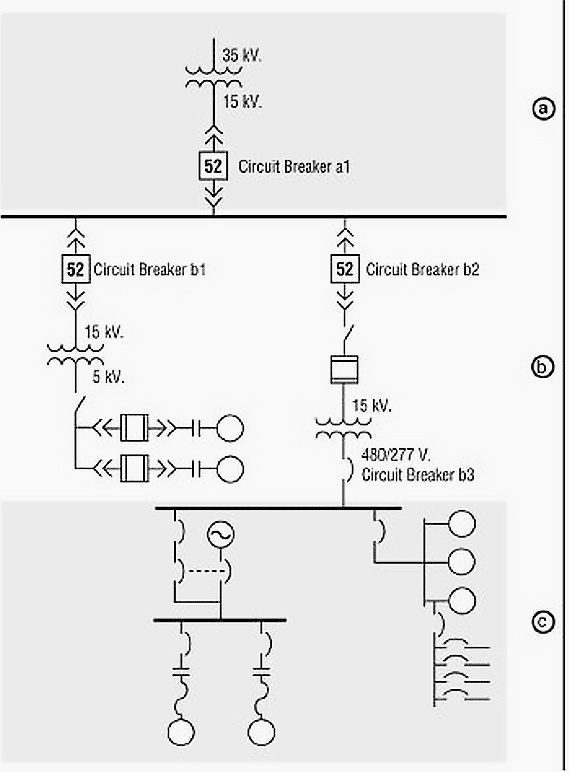
For smaller distributed systems, RS-485 remains a fundamental wiring layer. Unlike RS-232, RS-485 supports multiple devices on a shared balanced line running for hundreds of meters. Many industrial communication layers like Modbus RTU rely on RS-485 for its reliability and distance capability.
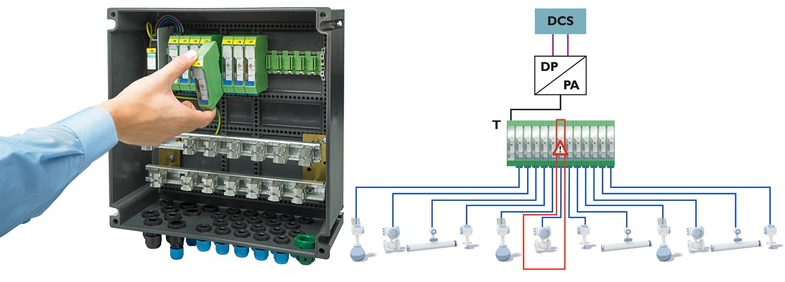
The emergence of IoT-enabled sensors has given rise to new data frameworks for connectivity. Industrial IO-Link protocol bridges simple sensors with digital networks, enabling the transmission of readings plus metadata through standard 3-wire cables. At higher layers, Message Queuing Telemetry Transport and OPC UA facilitate cloud integration, analytics, and machine-to-machine interaction, crucial for Industry 4.0.
Beyond the protocol rules, **wiring practices** determine signal quality. minimized EMI layout and structured grounding prevent data corruption. Differential signalingused in CAN and RS-485ensures noise cancellation by sending opposite signals that neutralize interference. Conversely, improper termination or loose connectors can cause data loss, reflection, or total failure.
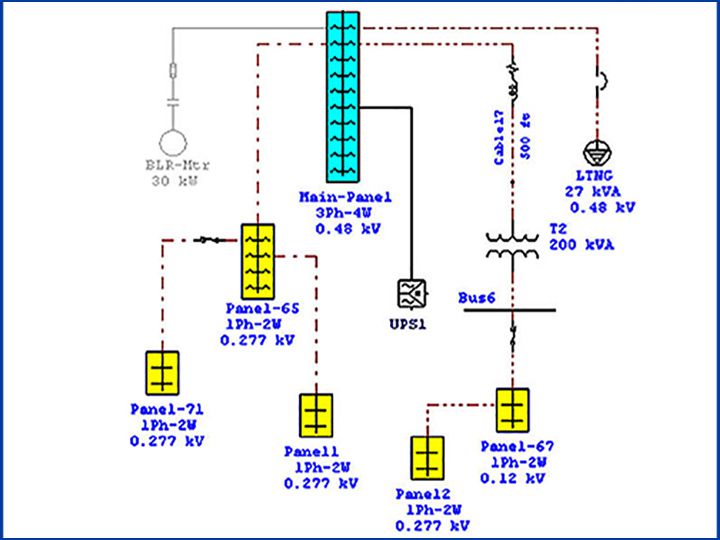
Modern networks integrate redundancy and diagnostics. Many systems include redundant lines that automatically take over if one fails. Devices also feature self-diagnostics, reporting network status and anomalies. Maintenance teams can access this data remotely, reducing troubleshooting time and improving operational continuity.
In the era of intelligent manufacturing, communication protocols are the neural network of automation. They let controllers, machines, and sensors share not only signals but also context and intelligence. Through standardized communication, systems can analyze performance and prevent failure.
By mastering industrial data networks, engineers move beyond connecting wiresthey create a common digital language across entire ecosystems. Every bit of data becomes a signal of coordination. Understanding that conversation is the key to intelligent design, and it defines what makes the next generation of electrical engineering.