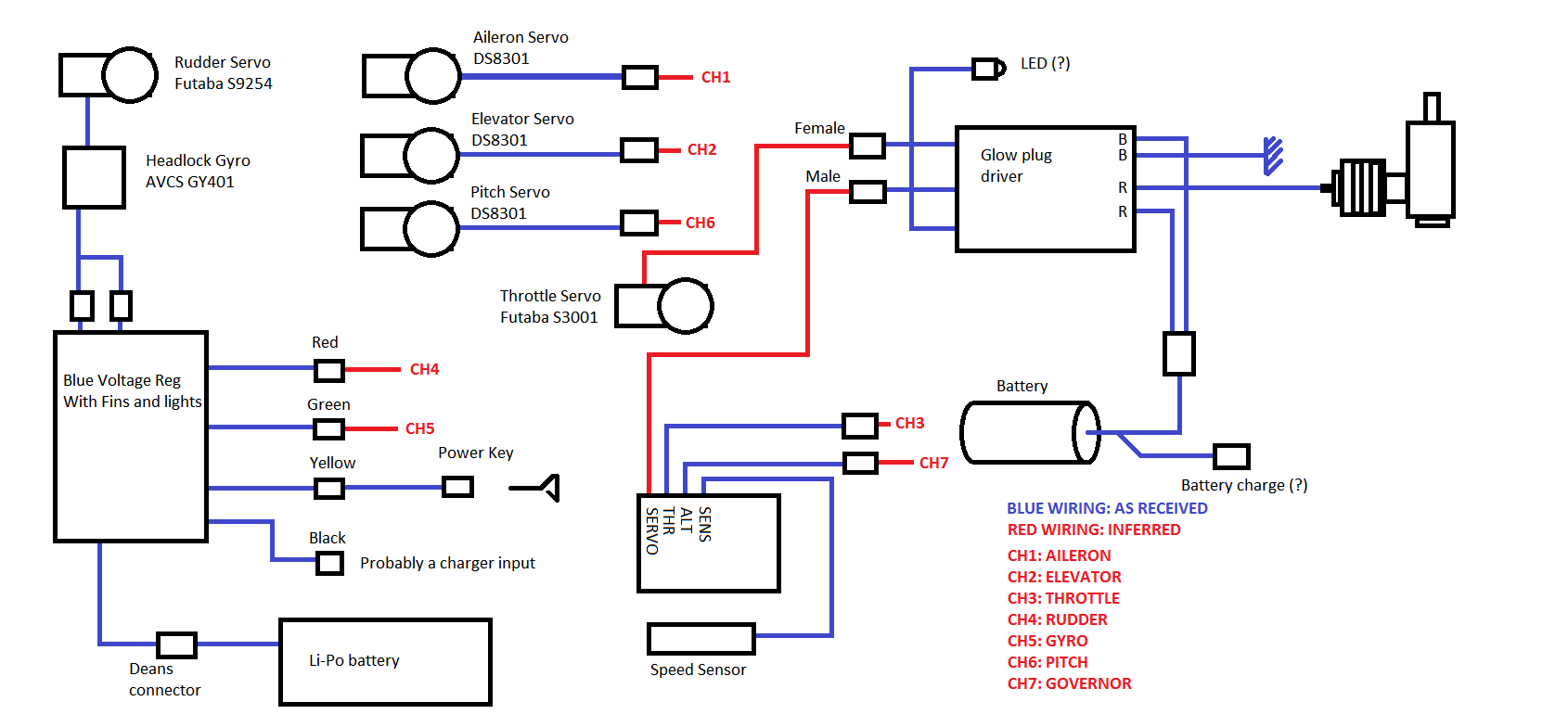
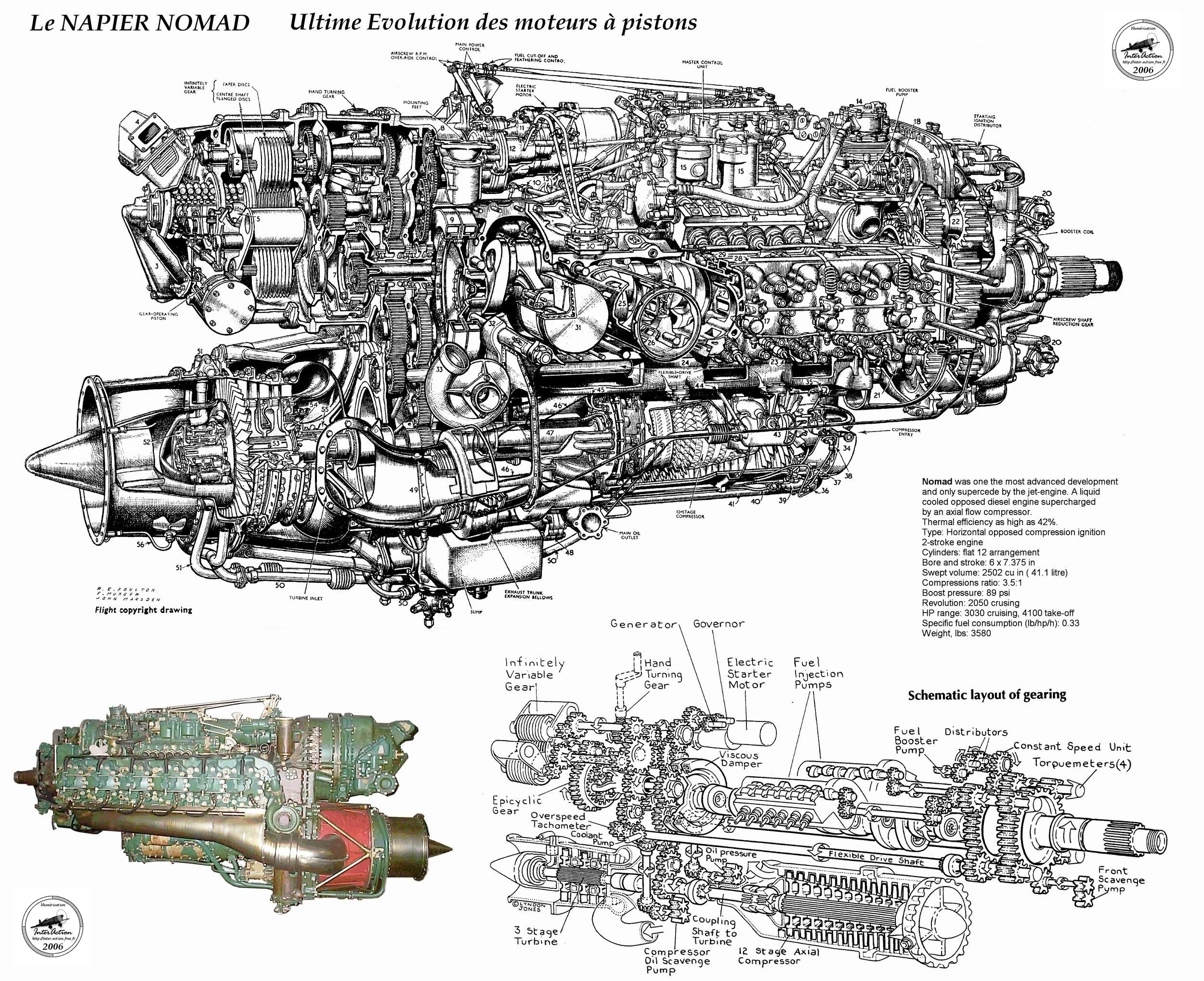
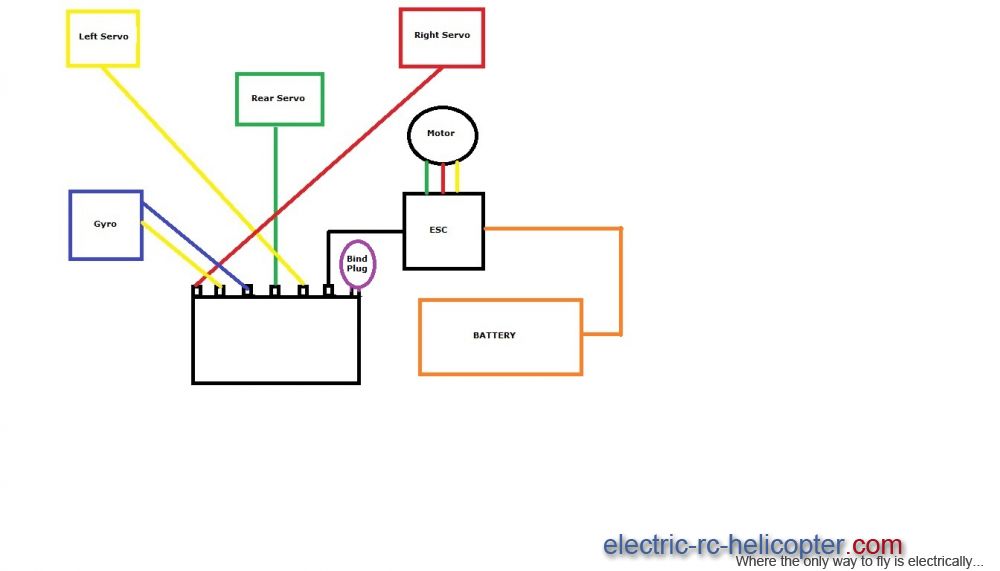
Accuracy in electrical work extends far beyond installation. The long-term safety, reliability, and maintainability of any system depend on its level of documentation, identification, and verification. Without organized records and consistent labeling, even a sophisticated design can become confusing and unsafe within months. Documentation and quality control transform a wiring job into a professional system.
### **The Role of Documentation**
Documentation is the technical record of an electrical system. It includes schematics, wiring diagrams, terminal lists, load tables, and revisions that describe how each cable, breaker, and contact connects and functions. Engineers rely on these records to understand logic, verify safety, and maintain systems.
Accurate documentation begins before the first wire is pulled. Each circuit must have a unique identifier that remains consistent between drawings and field labels. When changes occurrerouted cables, new junction boxes, or substitute partsthey must be reflected immediately in drawings. A mismatch between schematic and installation causes delays, confusion, and safety risks.
Modern tools like CAD or EPLAN software generate automatic drawings with standardized symbols. Many integrate with maintenance databases, linking each component to serial numbers, calibration logs, or test results.
### **Labeling and Identification**
Labeling turns documentation into visible reality. Every wire, terminal, and device should be uniquely identified so technicians can work safely without guessing. Proper labeling prevents misconnection and improves service quality.
Effective labeling follows these principles:
- **Consistency:** Use a unified numbering system across entire installations.
- **Durability:** Labels must withstand heat, oil, and vibration. Heat-shrink sleeves, laser engraving, or metal tags last longer than paper or adhesive stickers.
- **Readability:** Font and color contrast should remain clear in dim environments.
- **Traceability:** Every label must correspond directly to schematics.
Color coding adds instant recognition. standard IEC conductor colors remain common, while different colors separate control and power circuits.
### **Inspection and Verification**
Before energizing any system, conduct comprehensive validation. Typical tests include:
- Line and neutral verification.
- Insulation-resistance measurements.
- Conductor resistance and protection checks.
- Simulation of interlocks and relays.
All results should be documented in acceptance logs as baseline data for the assets lifecycle. Deviations found during tests must trigger corrective action and as-built updates.
### **Quality-Control Framework**
Quality control (QC) ensures build integrity from material to testing. It starts with incoming inspection of components and wiring materials. Supervisors check torque, bend radius, and routing. Visual inspections detect faults invisible in drawings.
Organizations often follow international quality management systems. These frameworks require inspection reports, calibration records, and technician certifications. Digital QC systems now allow technicians to upload test data and photos. Managers can monitor progress remotely, reducing delays and miscommunication.
### **Change Management and Revision Control**
Electrical systems rarely remain static. Components are replaced and extended over time. Without proper revision control, drawings quickly become outdated. Each modification should include a revision number, author, and date. As-built drawings must always reflect the final installed condition.
Version control tools synchronize field edits with design teams. This prevents duplicate work and data loss. Historical logs allow engineers to trace failures to their origin.
### **Training and Organizational Culture**
Even the best systems fail without disciplined people. Teams must treat documentation as a professional responsibility. Each recorded detail contributes to long-term reliability.
Training programs should teach labeling standards, documentation tools, and QC procedures. Regular audits help reinforce habits. routine field reviews confirm that records mirror reality. Over time, this builds a culture of precision.
Ultimately, documentation is not paperworkits professionalism. A system that is organized, traceable, and continuously updated remains safe, efficient, and serviceable. Good documentation keeps systems alive long after installation ends.