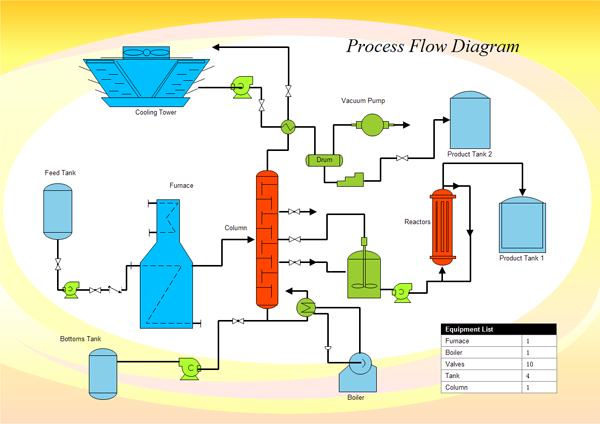
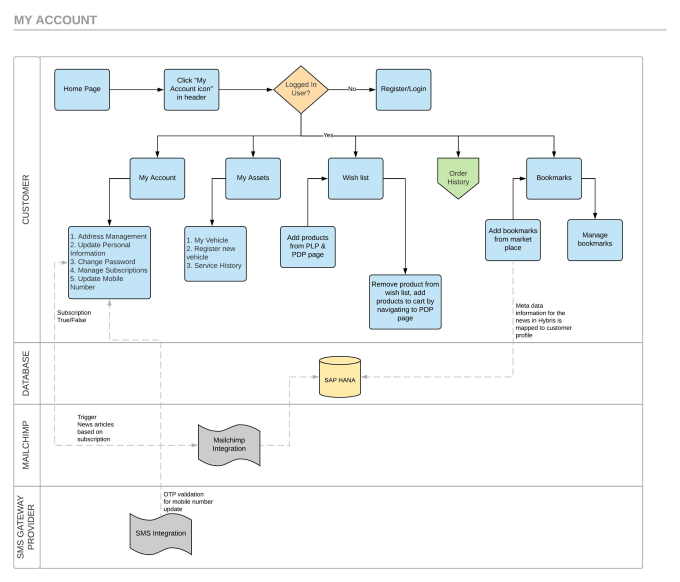
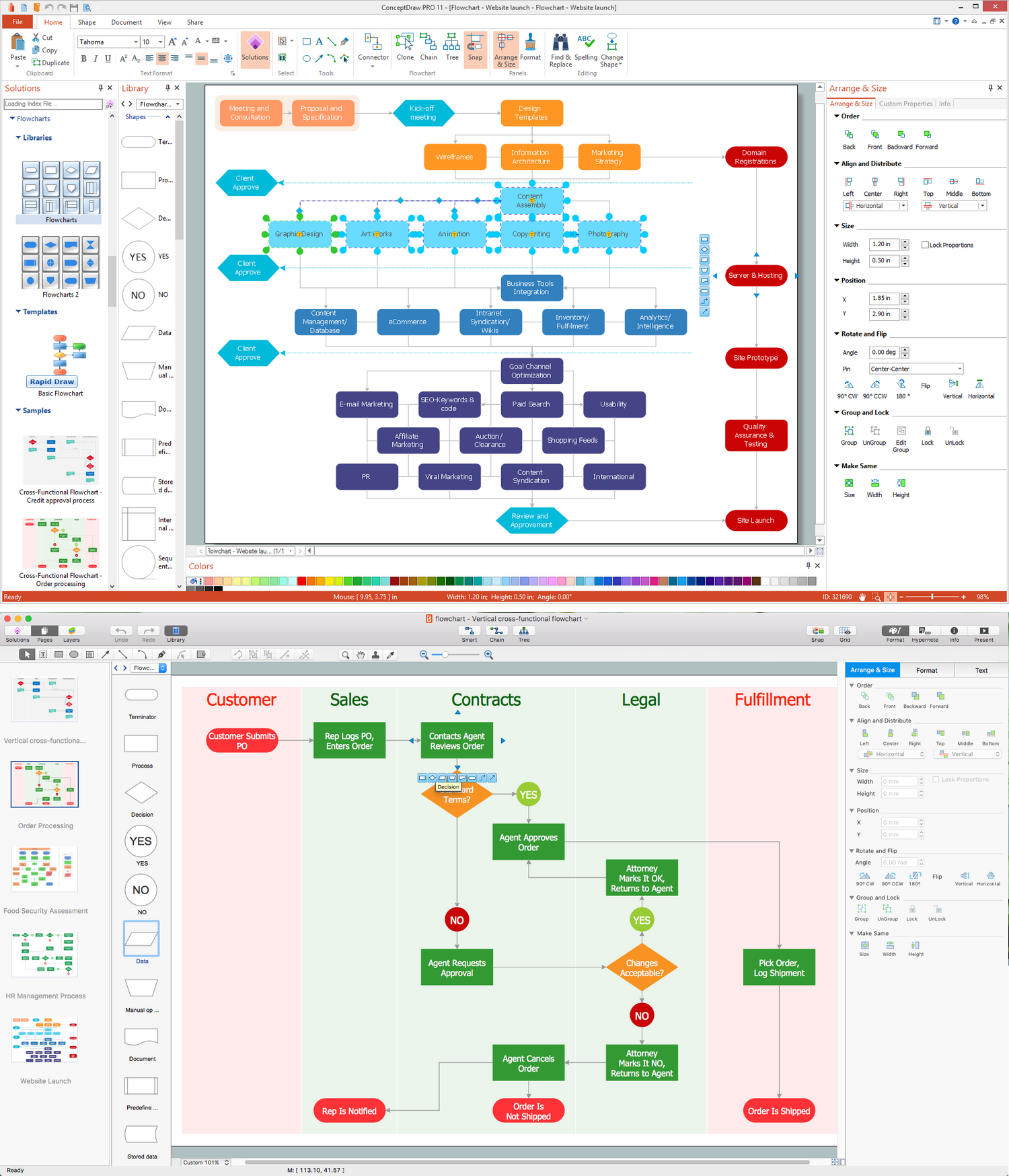
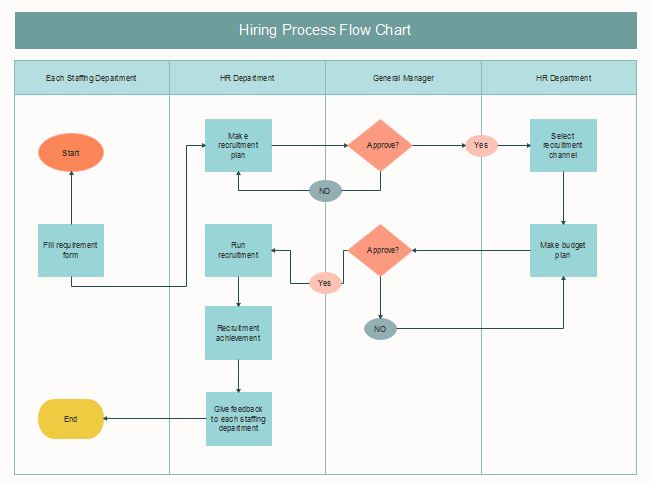
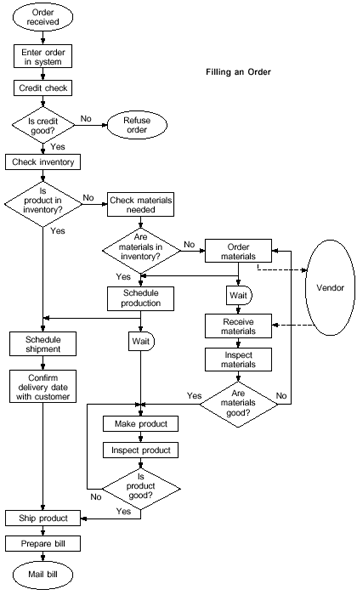
As devices evolve toward compact, high-frequency operation, maintaining waveform stability and interference control has become as critical as ensuring proper voltage and current flow. What once applied only to high-frequency communications now affects nearly every systemfrom automotive control modules to factory automation, robotics, and embedded devices. The accuracy and stability of a circuit often depend not only on its schematic but also on how its wiring interacts with the electromagnetic environment.
**Signal Integrity** refers to the maintenance of waveform accuracy and timing stability as it travels through wires, harnesses, and interfaces. Ideally, a digital pulse leaves one device and arrives at another unchanged. In reality, parasitic effects and noise coupling distort the waveform. Unwanted echoes, noise spikes, or skew appear when wiring is poorly designed or routed near interference sources. As systems move toward higher frequencies and lower voltages, even few nanoseconds of delay can cause logic errors or communication loss.
To ensure stable transmission, every conductor must be treated as a carefully tuned path. That means consistent impedance, minimal discontinuities, and short return loops. Twisted conductors and shielded lines are key design practices to achieve this. Twisting two conductors carrying opposite polarities cancels magnetic fields and reduces both emission and pickup. Proper impedance matchingtypically 100 O for Ethernetprevents reflections and distortion.
Connectors represent another vulnerable element. Even minuscule differences in pin spacing can alter impedance. Use connectors rated for bandwidth, and avoid sharing noisy and sensitive circuits within the same shell unless shielded. Maintain consistent crimp length and shielding continuity. In data-critical networks, manufacturers often define strict wiring tolerancesdetails that directly affect timing accuracy.
**Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)** extends beyond one wireit governs how the entire system interacts with its surroundings. A device must minimize emissions and maximize immunity. In practice, this means shielding noisy circuits, separating power and signal lines, and grounding carefully.
The golden rule of EMC is layout isolation and grounding control. High-current conductors and switching elements generate magnetic fields that couple into nearby signals. Always keep them orthogonal to data lines. Multi-layer grounding systems where a single bonding node (star ground) prevent unintended return currents. In complex setups like vehicles or industrial panels, braided ground straps or copper meshes equalize potential differences and reduce dropouts or resets.
**Shielding** is the primary barrier against both emission and interference. A shield blocks radiated and conducted noise before it reaches conductors. The shield must be bonded properly: both ends for high-frequency digital buses. Improper grounding turns protection into a noise source. Always prefer full-contact shield terminations instead of pigtails or partial connections.
**Filtering** complements shielding. Capacitors, inductors, and ferrite cores suppress spurious harmonics and EMI. Choose filters with correct cutoff values. Too aggressive a filter causes timing lag, while too weak a one fails to protect. Filters belong close to connectors or module interfaces.
Testing for signal integrity and EMC compliance requires both measurement and modeling. Scopes, analyzers, and reflectometers reveal ringing, jitter, and interference. Network analyzers identify reflections. In development, electromagnetic modeling tools helps engineers visualize field coupling and optimize layouts.
Installation practices are just as critical as design. Improper trimming or bending can alter transmission geometry. Avoid sharp bends, crushed insulation, or open shields. Proper training ensures installers preserve EMC integrity.
In advanced networks like autonomous vehicles or real-time control systems, data reliability is life-critical. A single bit error on a control network can halt machinery. Thats why standards such as automotive and industrial EMC norms define precise limits for emission and immunity. Meeting them ensures the system functions consistently and coexists with other electronics.
Ultimately, waveform fidelity and electromagnetic control are about predictability and stability. When every path and bond behaves as intended, communication becomes stable and repeatable. Achieving this requires mastering circuit physics, material design, and grounding science. The wiring harness becomes a precision transmission medium, not just a bundle of wirespreserving clarity in an invisible electromagnetic world.