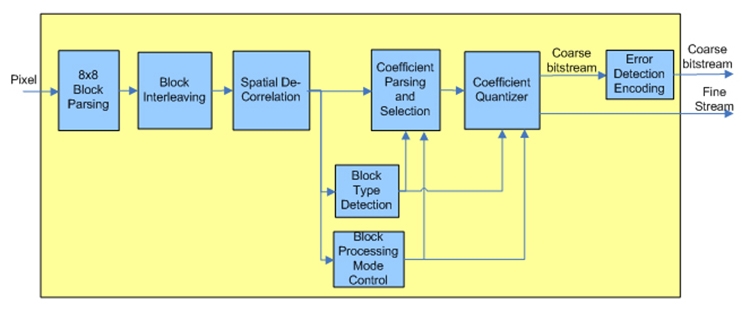
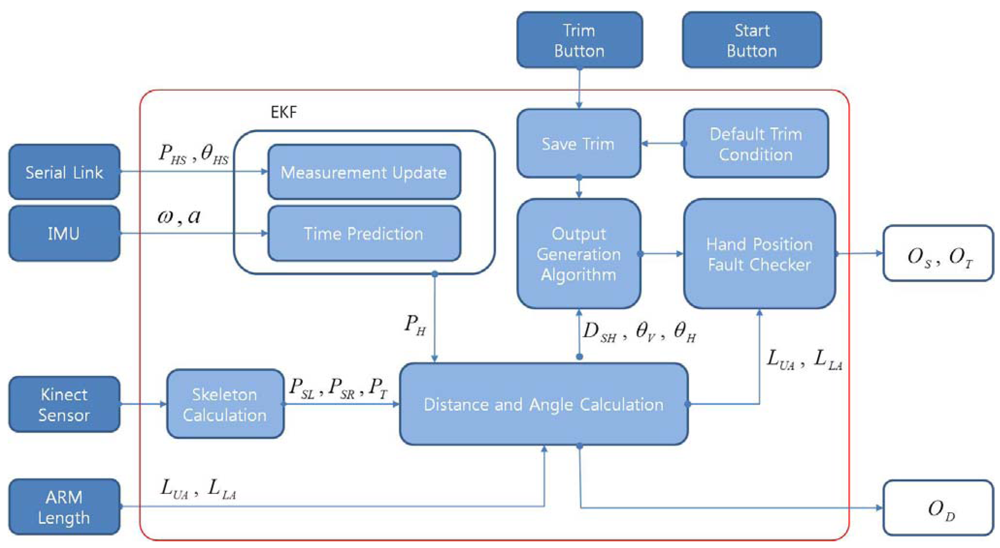
Todays complex electrical architectures have grown far beyond basic mechanical controls. They now include intelligent modules, processors, and networked controllers, all linked via layered wiring systems. Diagnosing faults in such systems requires more than intuition or experienceit demands a logical process supported by accurate tools. Without a systematic approach, troubleshooting quickly turns into guesswork that drains efficiency and reliability.
Diagnostics is the art and science of comparison. It observes how a system performs under design conditions compared to reality. Success begins by defining known-good baselines: voltage, waveform, or logic state. Each data point captured offers clues that, when combined, reveal the precise fault origin.
### **1. Fundamental Tools**
The foundation of every diagnostic process is the universal measuring instrument. It measures voltage, current, and resistance with precision and speed. Whether youre checking power rails, earth paths, or resistor values, the DMM provides instant validation of circuit health. Its beeper and forward-bias tests quickly expose broken links or polarity faults.
The scope extends measurement into the dynamic realm. It reveals how voltage changes with time, displaying pulses, oscillations, and switching behaviors. For digital control or analog modulation, oscilloscopes visualize distortion, missing pulses, or delay. Multi-channel scopes can align multiple signals to assess propagation delay or synchronization.
Clamp meters measure current non-invasively. They use magnetic induction to detect current magnitude and direction, ideal for energized installations. Modern DC-capable models reveal inrush or leakage current that static tests may miss.
### **2. Advanced Diagnostic Instruments**
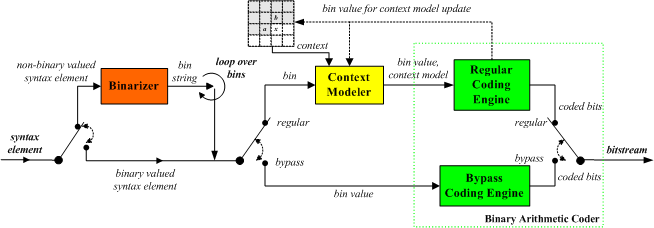
When basic tools arent enough, technicians turn to specialized analyzers and testers. digital decoders capture serial communication like CAN, LIN, or UART, translating bits into structured messages. This is vital when modules communicate and simple measurements cant explain failures.
Meggers apply DC stress tests to detect leakage or weak insulation. In critical systems, this prevents catastrophic insulation failure.
Cable analyzers locate breaks, impedance changes, or shorts. Theyre indispensable for high-end communication cables.
At component level, LCR meters measure electrical parameters with high accuracy. This detects coil imbalance. infrared imagers visualize heat signatures, instantly exposing hotspots invisible to meters.
### **3. Measurement Strategy**
Tools mean little without method and order. Effective troubleshooting follows a structured path:
- **Visual Inspection:** Look for physical damage, wear, or contamination. Over half of faults are found visually.
- **Power & Ground Verification:** Confirm voltage supply and low resistance returns. Many faults hide in poor grounds.
- **Signal Analysis:** Compare transitions and duty cycles during real operation.
- **Comparative Testing:** cross-check similar circuits.
- **Functional Simulation:** Replicate operating conditions to confirm repairs.
Record every reading. Documentation creates traceable knowledge, turning data into predictive maintenance.
### **4. Safety and Calibration**
Safety ensures accuracy. Before testing, check insulation and tips. Calibrate instruments regularly to avoid drifted readings. Always respect CAT ratings: never use a low-rated meter on high-energy systems. For energized HV systems, use specialized isolation accessories.
### **5. Data Integration and Modern Trends**
Diagnostics is becoming digitally connected. IoT-enabled meters and scopes stream data directly to the cloud. This enables real-time supervision and automated alerts. Automated Test Systems (ATS) now perform hundreds of tests per second, ensuring consistency and reproducibility. Combined with machine learning algorithms, they predict weak points before failures occur.
### **6. The Human Element**
Despite automation, the human mind remains irreplaceable. Instruments show numbers, but expertise gives context. Skilled engineers connect physical signs with electrical evidence. They know that a strange voltage or waveform may be a symptom, not the root cause. Effective diagnosis combines reasoning with field sense.
Ultimately, the goal is not just to measure, but to understand. The right tools amplify insight, turning invisible electricity into knowledge. Mastering measurement transforms random faults into predictable phenomenathe essence of true technical expertise.