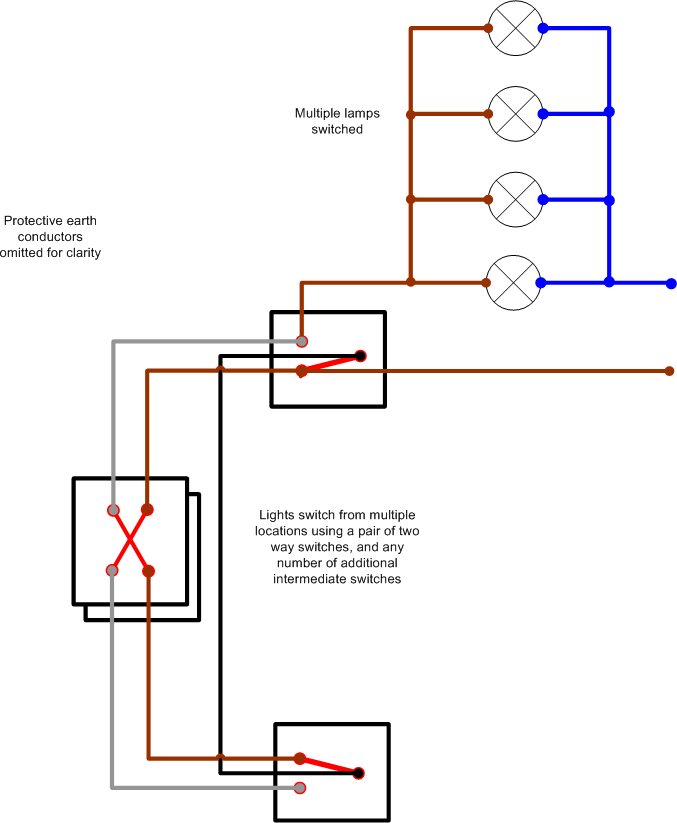
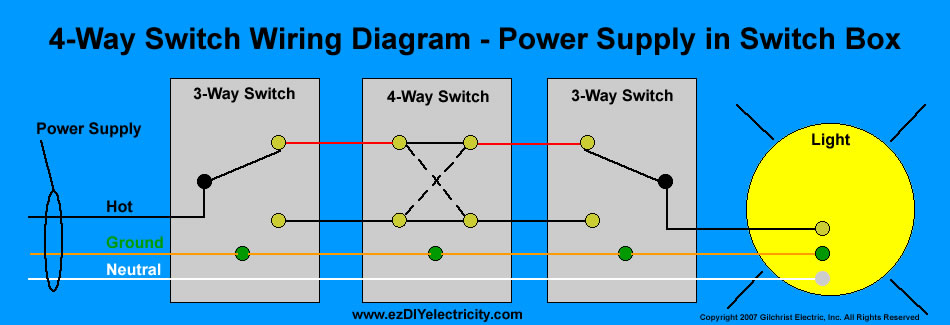
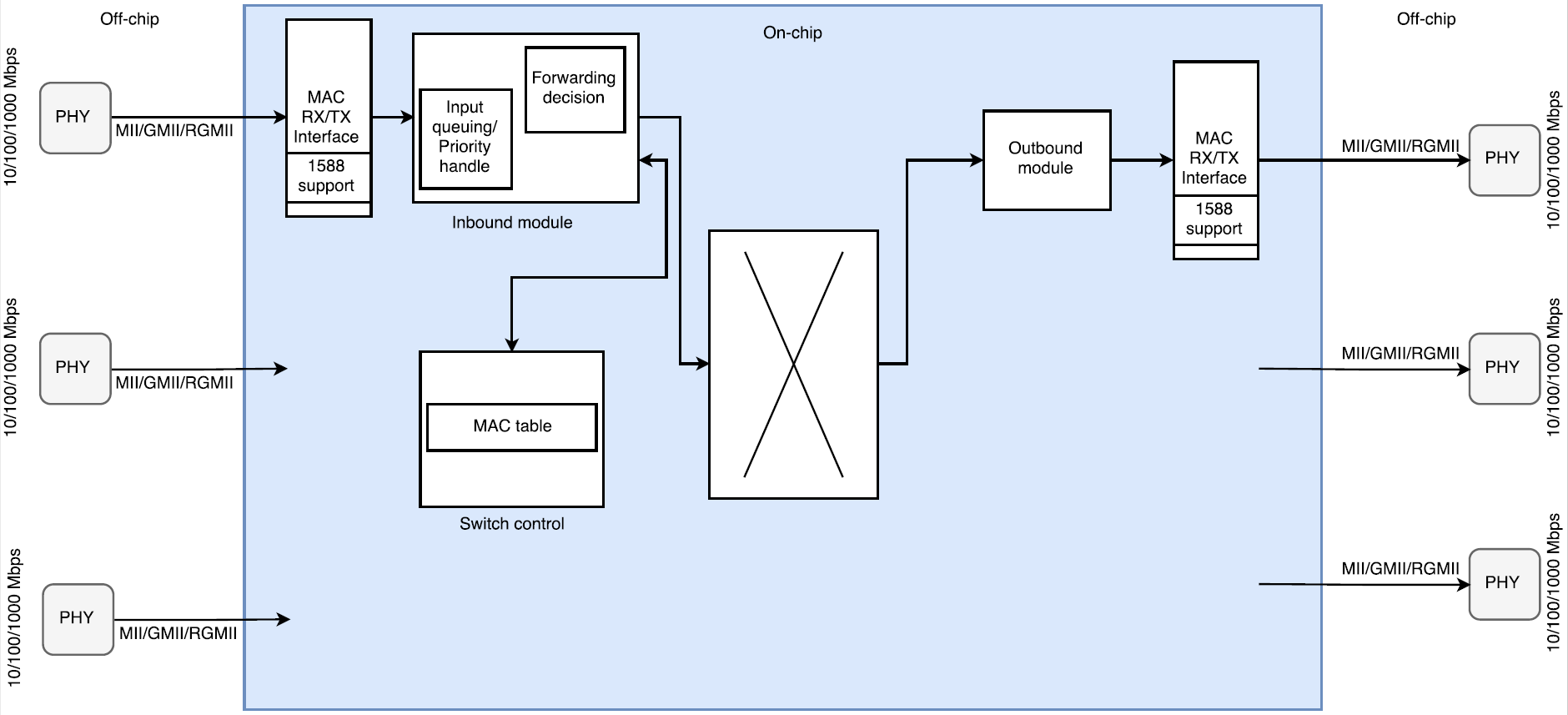
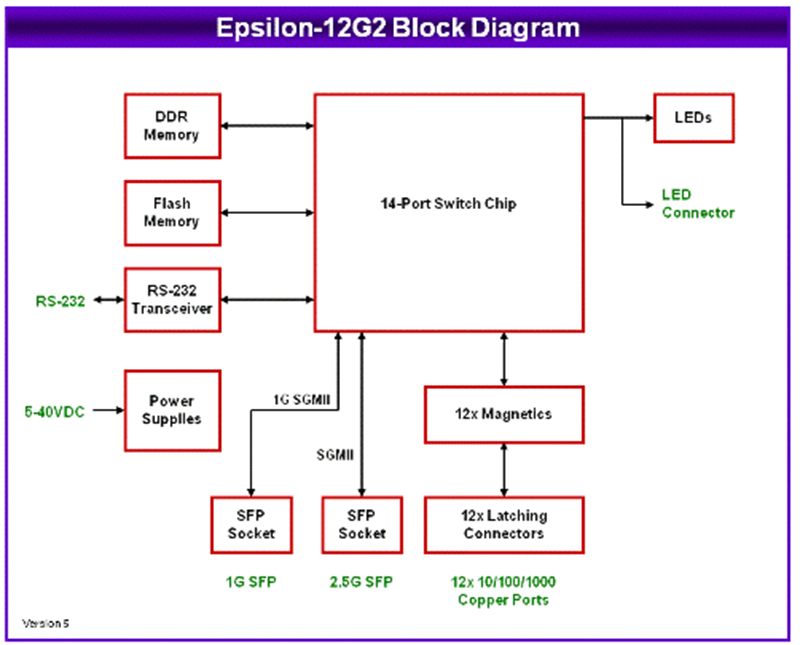
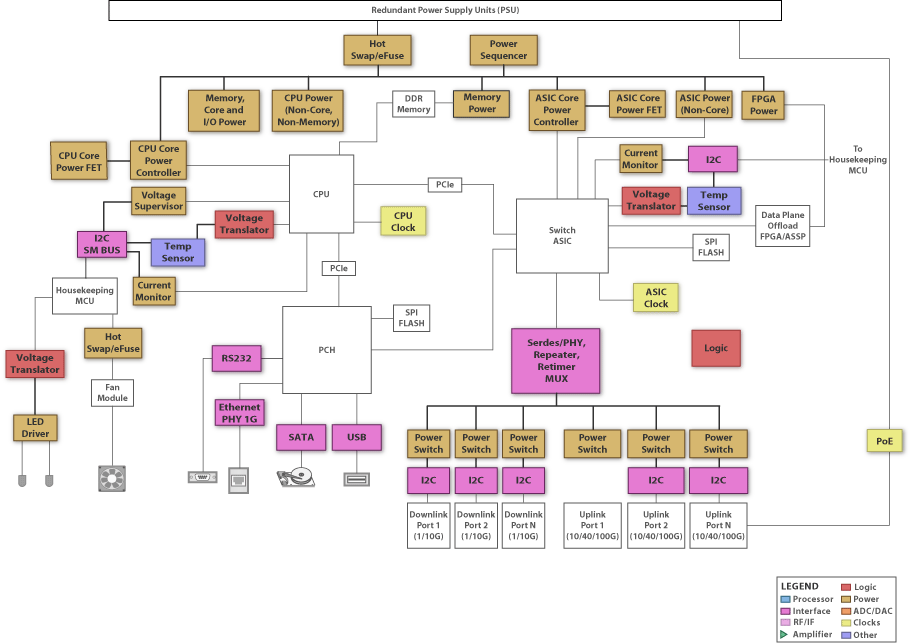
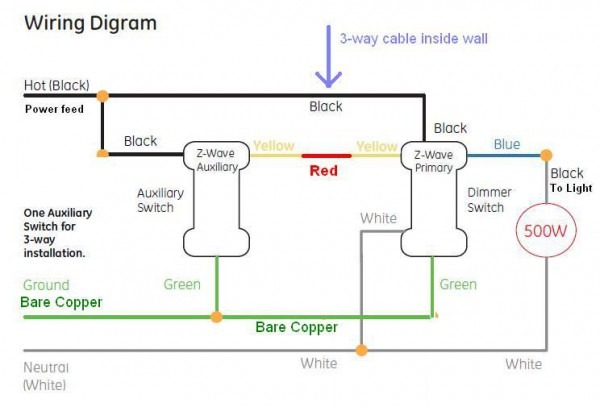
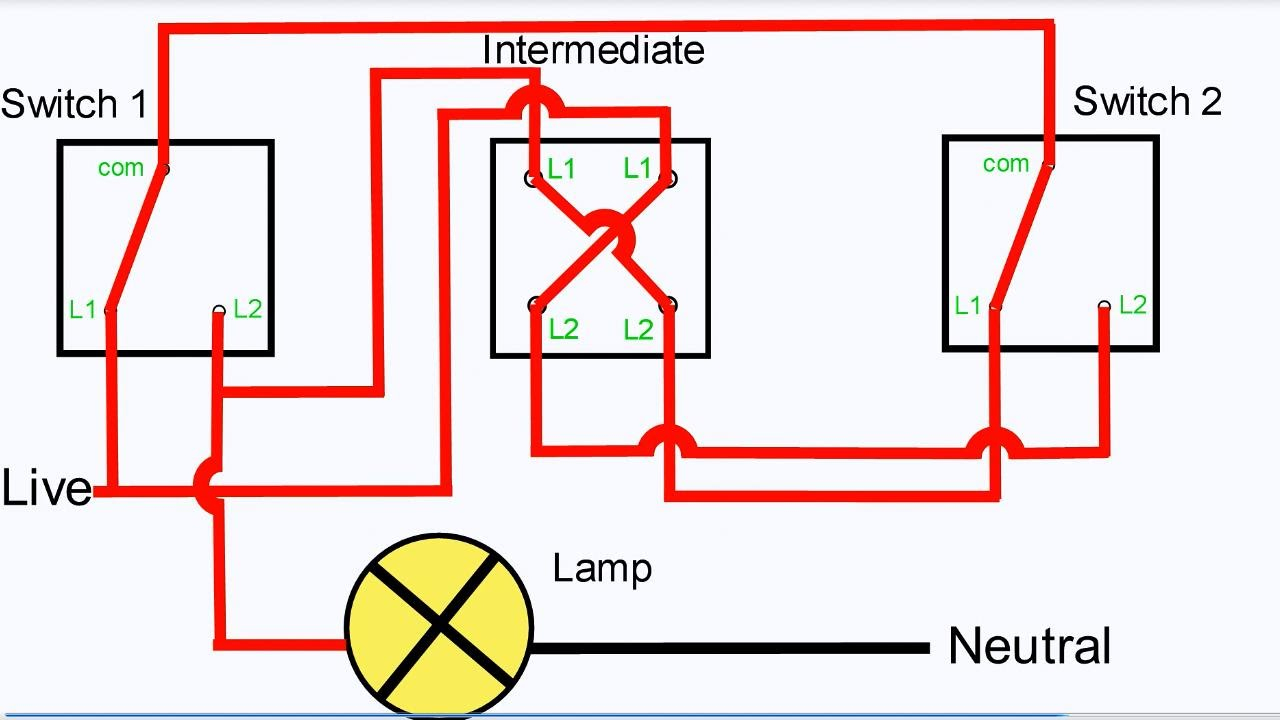
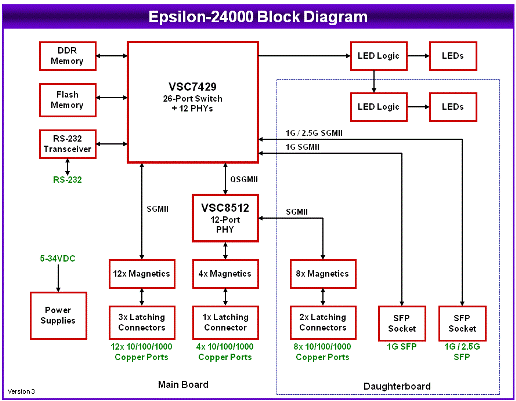
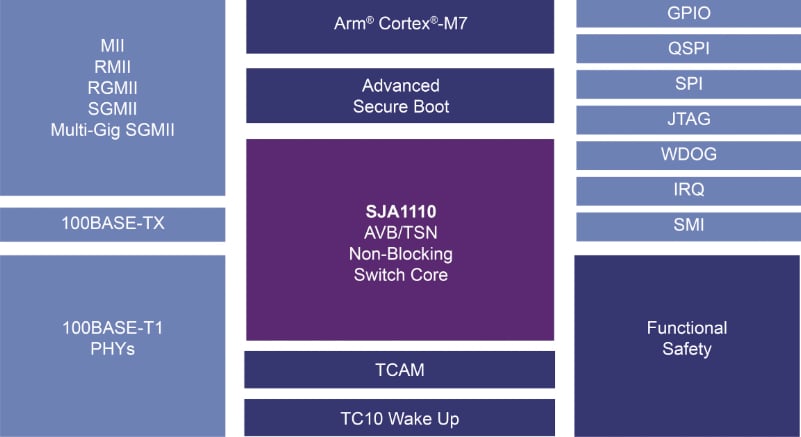
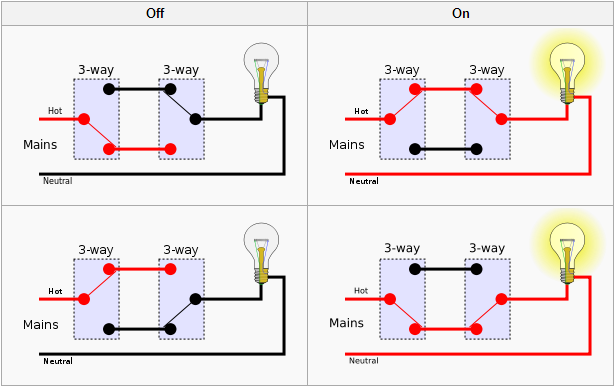
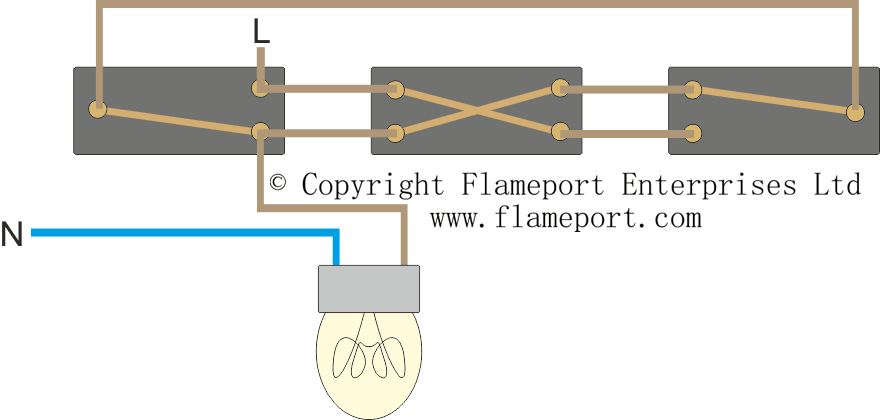
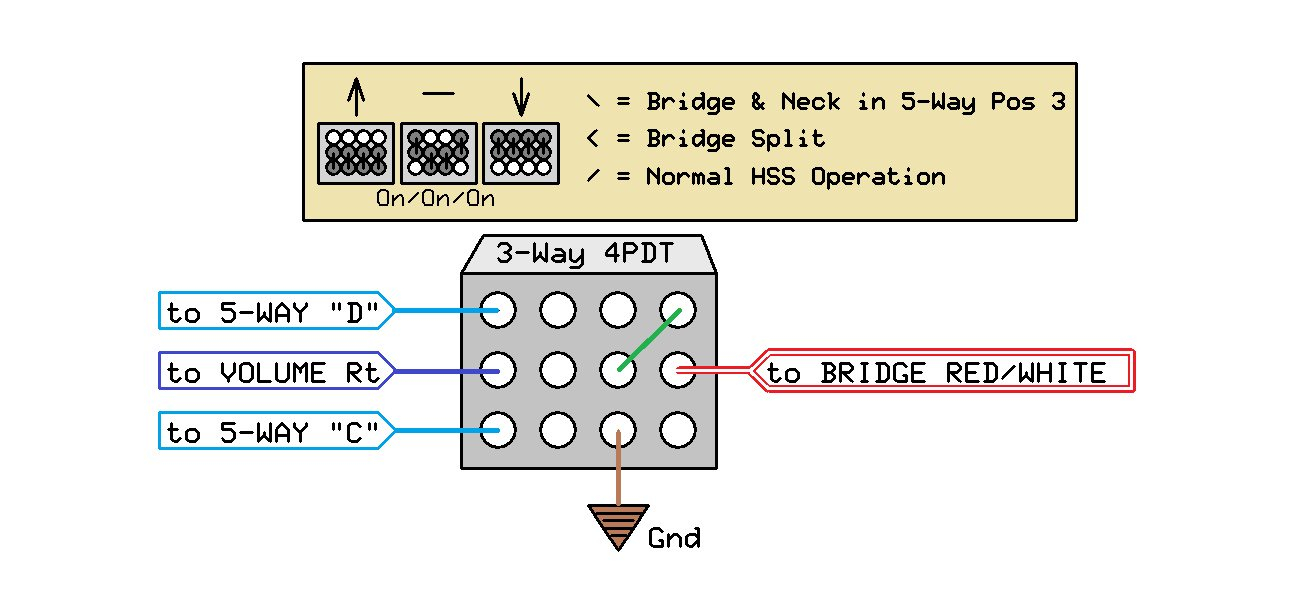
The world of wiring is undergoing a transformation. What was once an inert power distribution web carrying only electricity and signals has now become an active, data-driven infrastructure. These modern systems can monitor, communicate, and adapt in real time. The rise of intelligent harnesses and Internet of Things connectivity has reshaped wiring philosophy across industriesfrom vehicles to buildings to factories.
At the core of this evolution lies a shift toward total interconnection. Old wiring could not report its health or performance, built only to carry current without awareness. Smart systems, however, embed intelligence and measurement at every node. These devices measure voltage, current, temperature, and vibration and report real-time status to centralized or remote systems. The result is a responsive electrical architecture that not only delivers energy but also monitors its own well-being.
This capability is especially critical in high-reliability or mission-critical infrastructure. In manufacturing environments, smart harnesses can detect early warning signs such as abnormal current draw or heat buildup. In next-generation automotive systems, IoT-enabled intelligent fuse boxes communicate with onboard diagnostics, isolating issues before they escalate. The fusion of hardware, software, and analytics is what truly makes wiring smart.
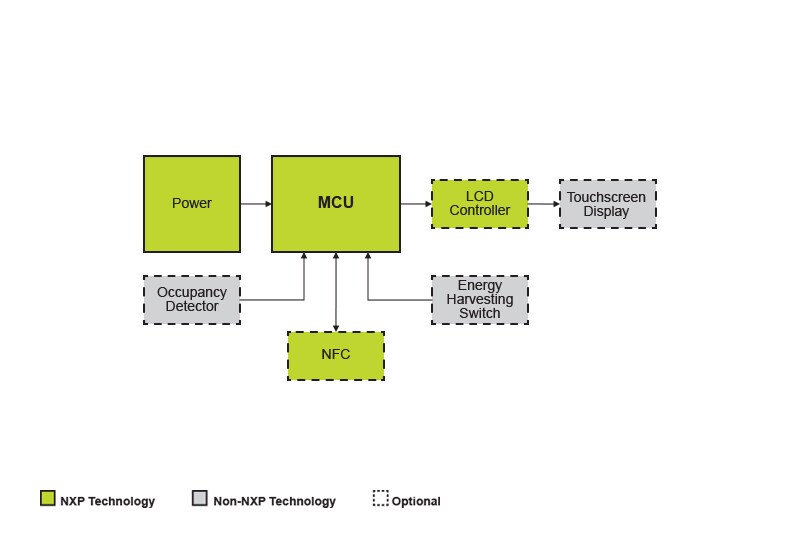
### **Key Components of Smart Wiring**
- **Embedded Sensors:** Tiny transducers capture voltage, strain, or thermal data. They alert engineers before damage occurs by observing environmental variations and current shifts.
- **Microcontrollers and Edge Processors:** Local processors analyze data directly within the harness. This allows real-time fault reaction.
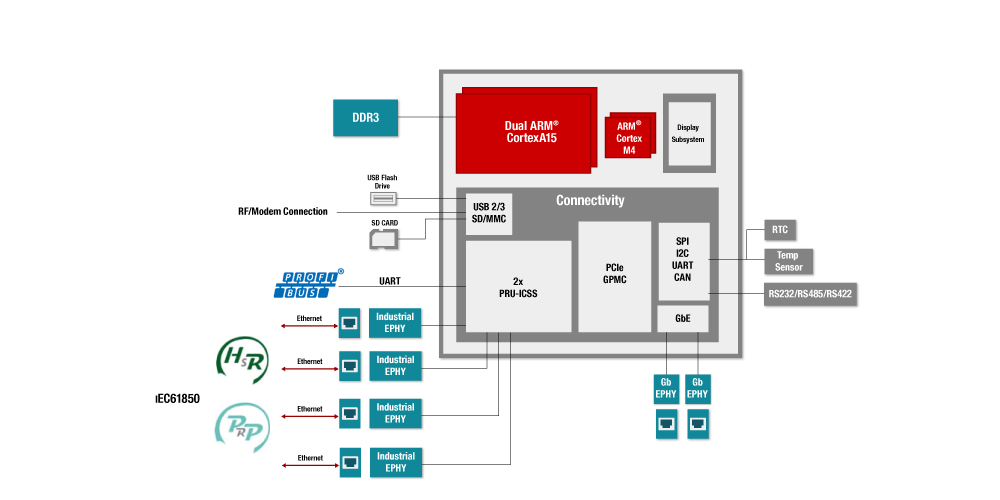
- **Communication Interfaces:** wired and wireless protocols link distributed nodes and gateways for coordinated system awareness.
- **Power Electronics Integration:** Solid-state relays, digital fuses, and electronic switches dynamically regulate current flow, replacing mechanical breakers.
Together, these components create a living network of intelligenceone where every wire can sense, think, and communicate.
### **IoT Connectivity and Cloud Integration**
The IoT ecosystem extends wiring intelligence far outside the control cabinet. Through cellular, Wi-Fi, or LAN connections, wiring data streams into monitoring servers. Predictive algorithms then analyze voltage, current, and thermal behavior. Operators and engineers receive alerts on tablets and cloud consoles, enabling preemptive repairs before faults propagate.
In intelligent infrastructure, IoT-integrated wiring connects lighting, HVAC, and energy systems under a unified automation hub. Sensors automatically regulate systems for efficiency. In remote solar and wind networks, data-driven harnesses transmit environmental and performance metrics.
### **Design Considerations for Smart Wiring**
Embedding intelligence introduces fresh design constraints. Each sensor and microcontroller demands stable voltage and reliable data pathways. Designers must maintain EMI control while preserving mechanical robustness. Hybrid cables often combine supply and communication lines, saving space while minimizing cross-talk.
Power management is crucial. Smart nodes continuously draw small currents, so systems must support energy-efficient operation. Some designs even recycle ambient energy to sustain sensors.
Cybersecurity becomes part of the electrical design. Encryption, authentication, and firmware verification prevent data tampering or unauthorized access.
### **Applications Across Industries**
- **Automotive:** Electric and autonomous vehicles depend on intelligent wiring to manage power and data distribution. Each module reports live performance metrics to onboard diagnostics.
- **Aerospace:** Intelligent aerospace cabling reduce maintenance effort under harsh flight environments.
- **Industrial Automation:** Condition-monitoring cables detect wear and insulation breakdown in robots, conveyors, or production lines.
- **Smart Buildings:** IoT-linked wiring enables automated lighting and energy management.
- **Renewable Energy:** Solar farms and wind turbines use smart wiring to detect insulation leakage and load imbalance.
### **Diagnostics and Predictive Maintenance**
The biggest advantage of smart wiring lies in data-driven self-analysis. Instead of scheduled inspections, systems now monitor themselves constantly. Predictive analytics engines identify early indicators of degradation such as temperature rise and abnormal waveform distortion.
For instance, an IoT-connected harness can self-isolate faults to maintain uptime. Combined with cloud analytics and visualization dashboards, entire facilities can be supervised globally, minimizing cost and reducing maintenance waste.
### **The Future of Wiring Intelligence**
As artificial intelligence and nanotechnology progress, wiring will evolve into adaptive, regenerative systems. Self-repairing insulation, dynamic voltage balancing, and adaptive routing are already emerging in prototypes. Soon, wiring systems may adjust pathways on demand and learn load behavior over time.
Ultimately, smart wiring fuses hardware, software, and intelligence. It turns ordinary wire into a digital organ within a connected ecosystem. For technicians and engineers, mastery now means understanding both current and code. When cables can communicate, systems can truly think.